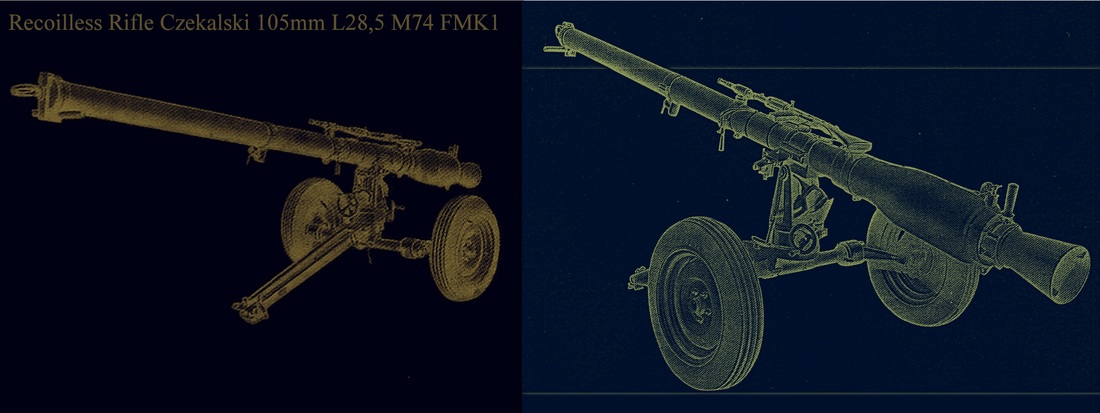
Infantry Support Weapons: Grenades, Mortars, Light Cannons and Machine Guns
Colt-Browning M1917 A.A with m37 mount.
M36 Pirelli gas mask type US Army M1A1/2 Kops, Tisson style, (without cannister box and filter), from 1936, Argentine Industry.
During Malvinas Campaign, Argentina used the US Army/USMC Mask Field M-17 series (The M17 series includes three types of masks, the M17, M17A1 and M17A2 Chemical-Biological)), with M1956 carrier and protective cover (Argentine Army); The USN Navy, ND Mark IV Gas Mask, (Argentine Navy and Marines Infantry); The FAA/AAF Argentine Air Force, (Some Finnish or Israeli Model ?, Chinese MF 14?), type QBN - MSA Full-Face Respirator, Gas-Mask and cannister box. 1990s, US M-40 Gas Mask ?
During Malvinas Campaign, Argentina used the US Army/USMC Mask Field M-17 series (The M17 series includes three types of masks, the M17, M17A1 and M17A2 Chemical-Biological)), with M1956 carrier and protective cover (Argentine Army); The USN Navy, ND Mark IV Gas Mask, (Argentine Navy and Marines Infantry); The FAA/AAF Argentine Air Force, (Some Finnish or Israeli Model ?, Chinese MF 14?), type QBN - MSA Full-Face Respirator, Gas-Mask and cannister box. 1990s, US M-40 Gas Mask ?
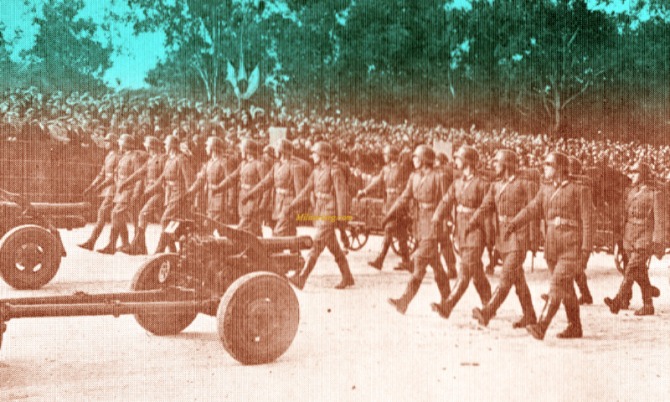
Argentine, NCO Magazine "Revista del suboficial 1940s".
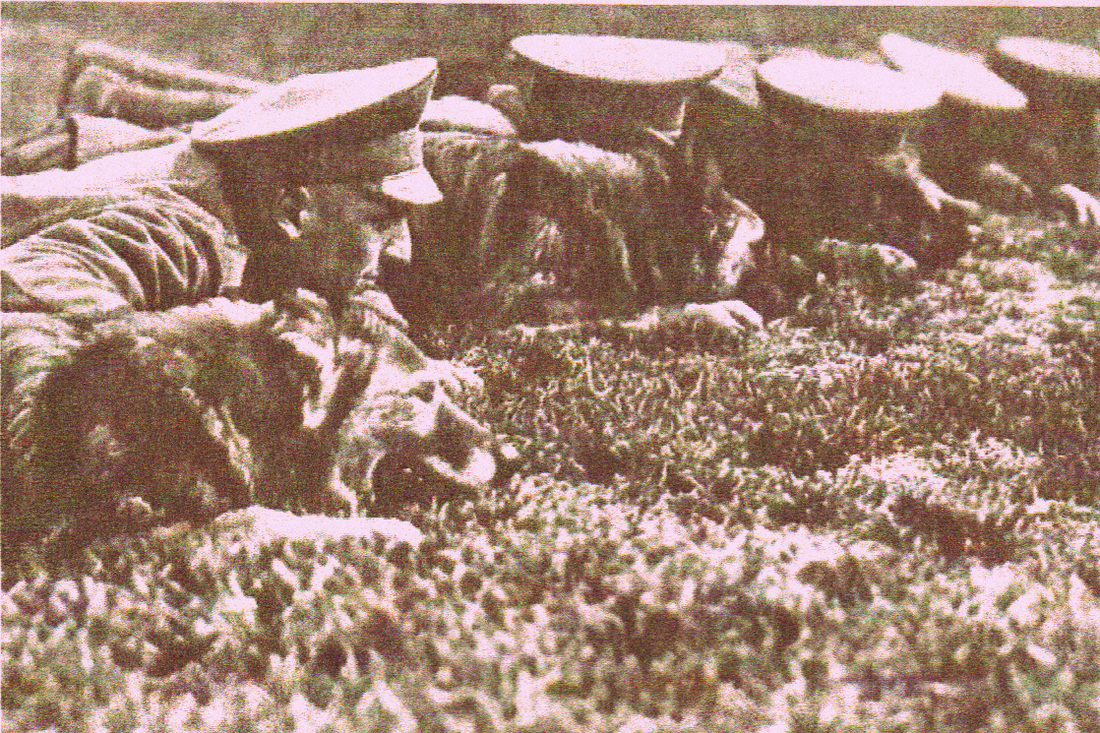
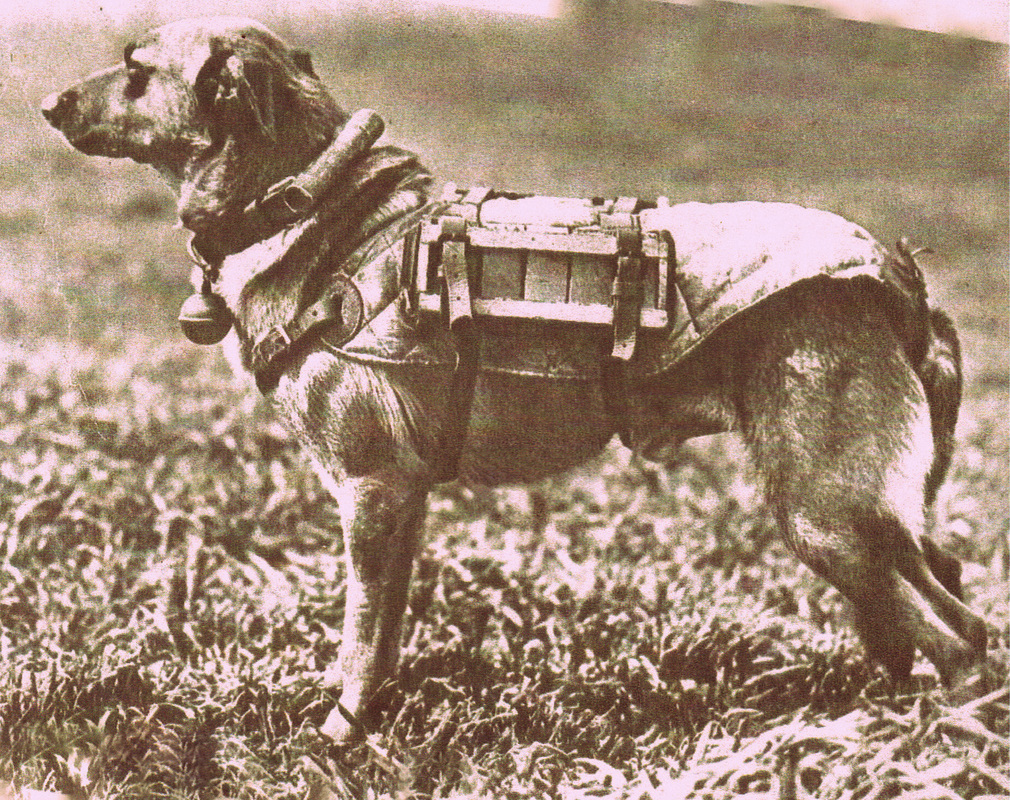
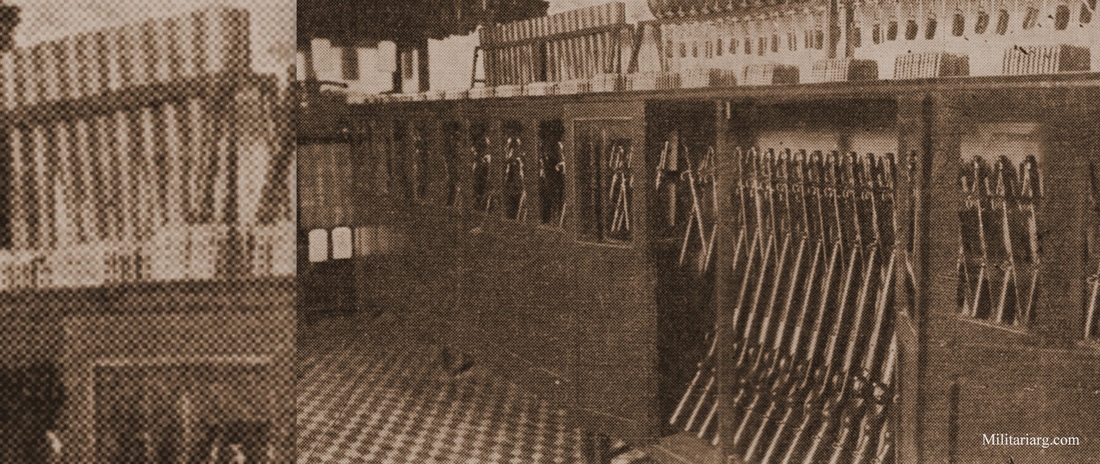
War Dogs
War Dog carrying rifle ammunition boxes for the advanced lines. Note the Egg Hand Grenade below thc collar and the tubular mail canister. Photo: Caras y Caretas 1935.
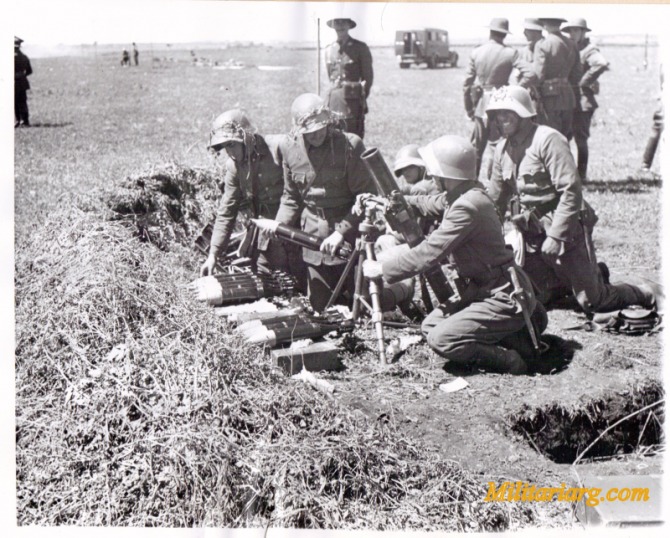
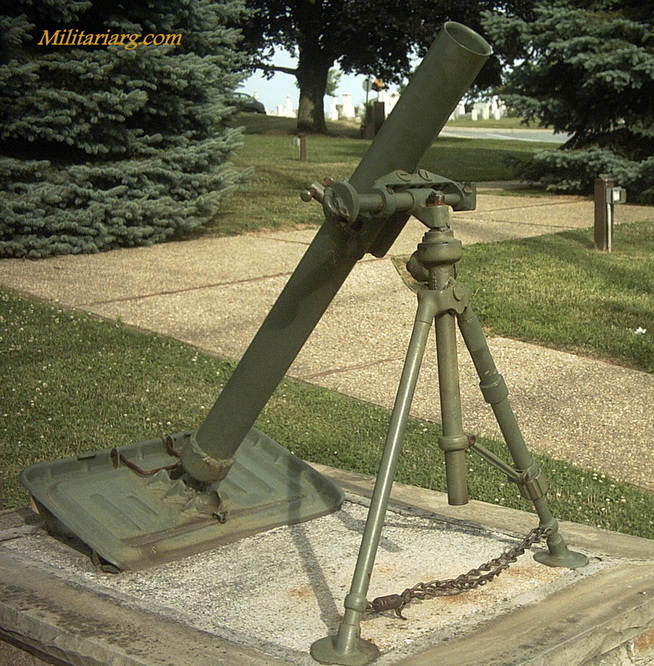
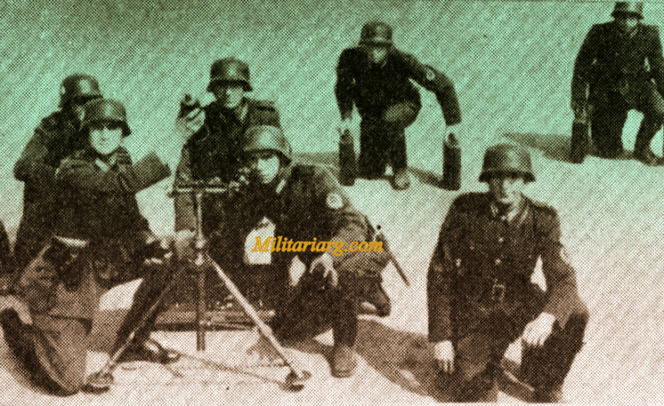
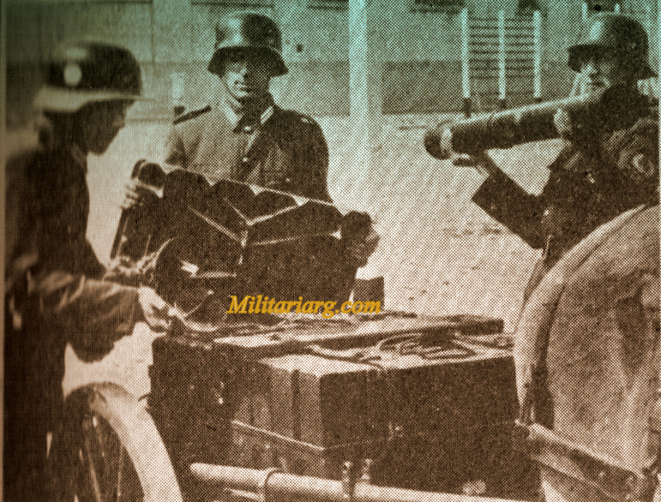
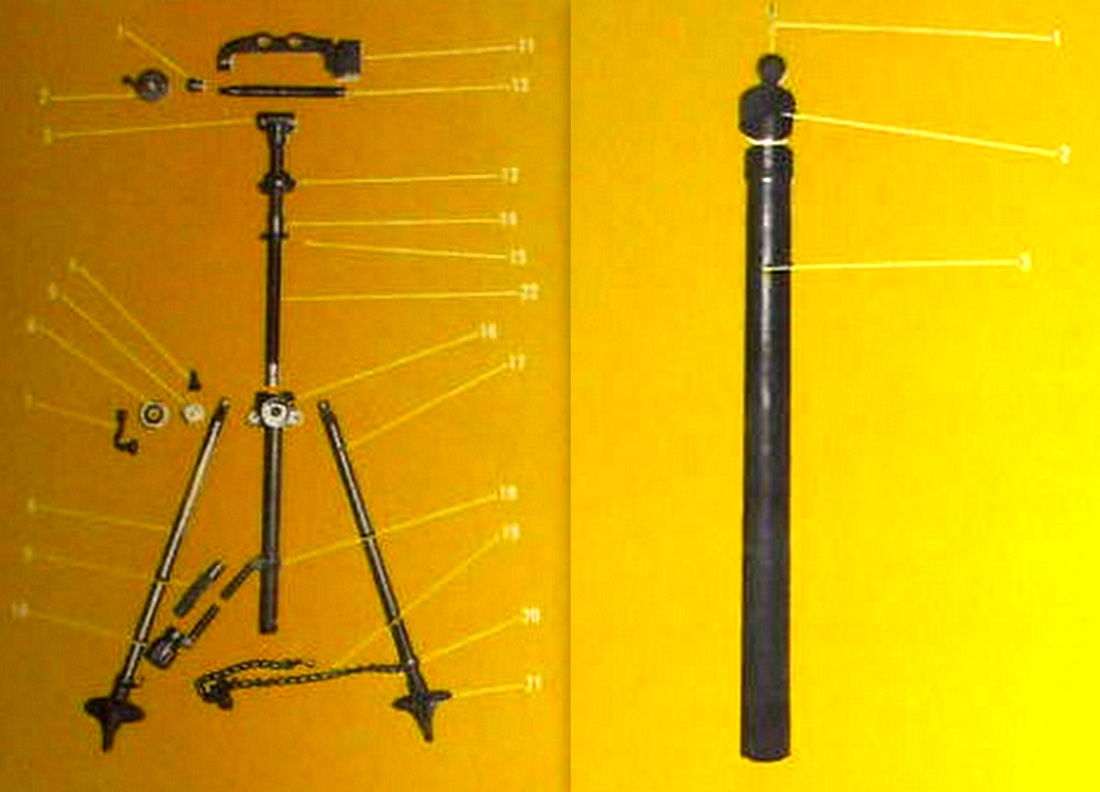
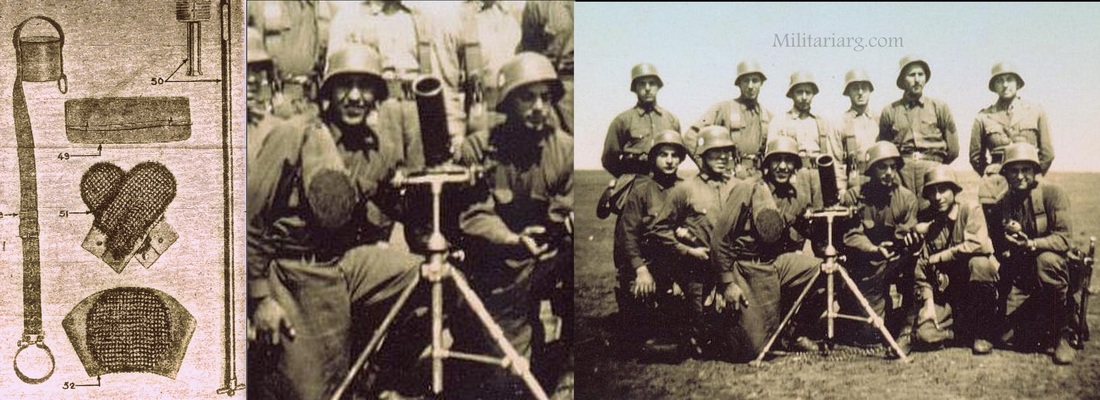
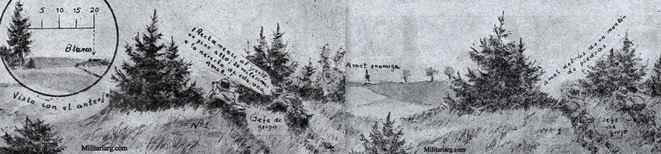
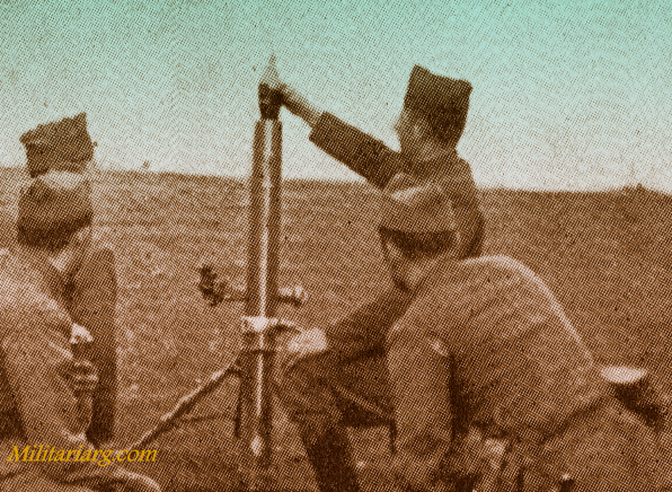
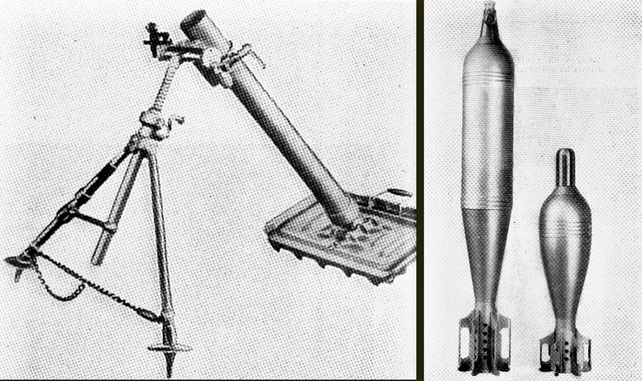
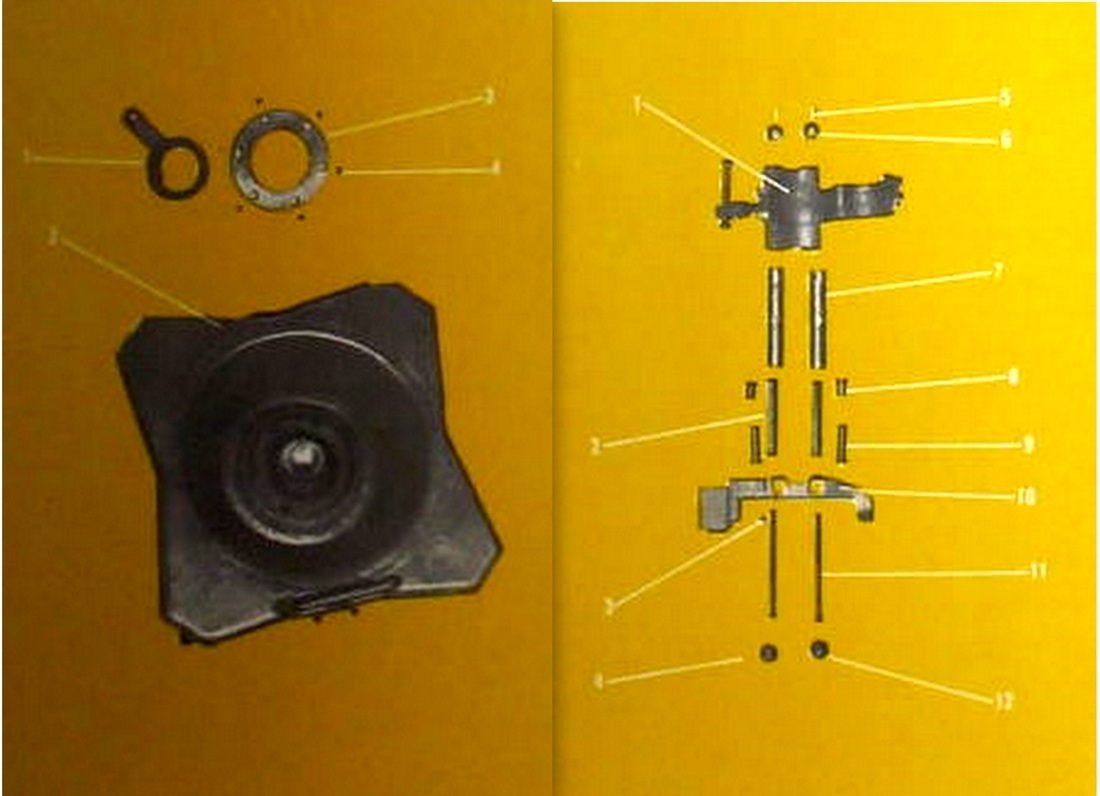
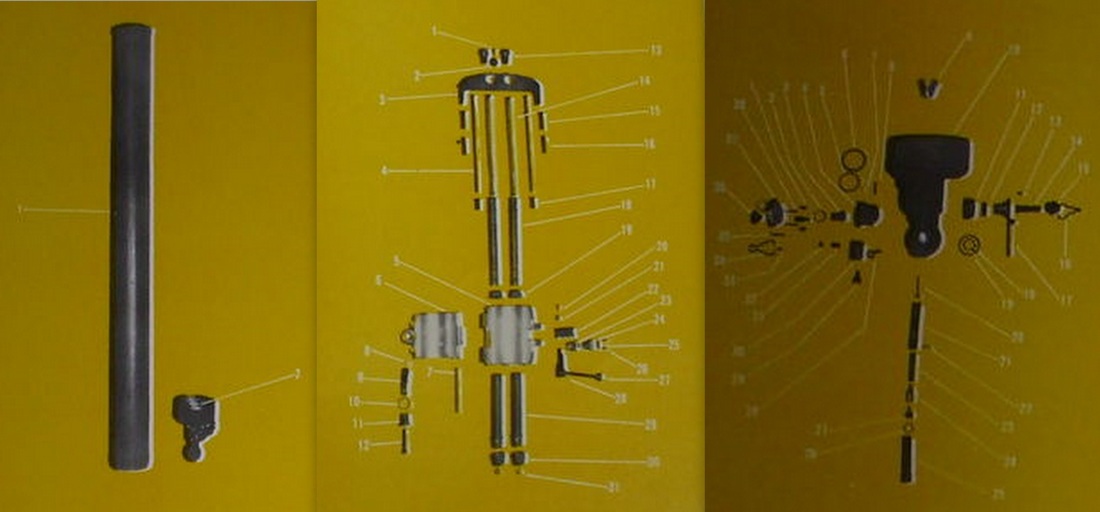
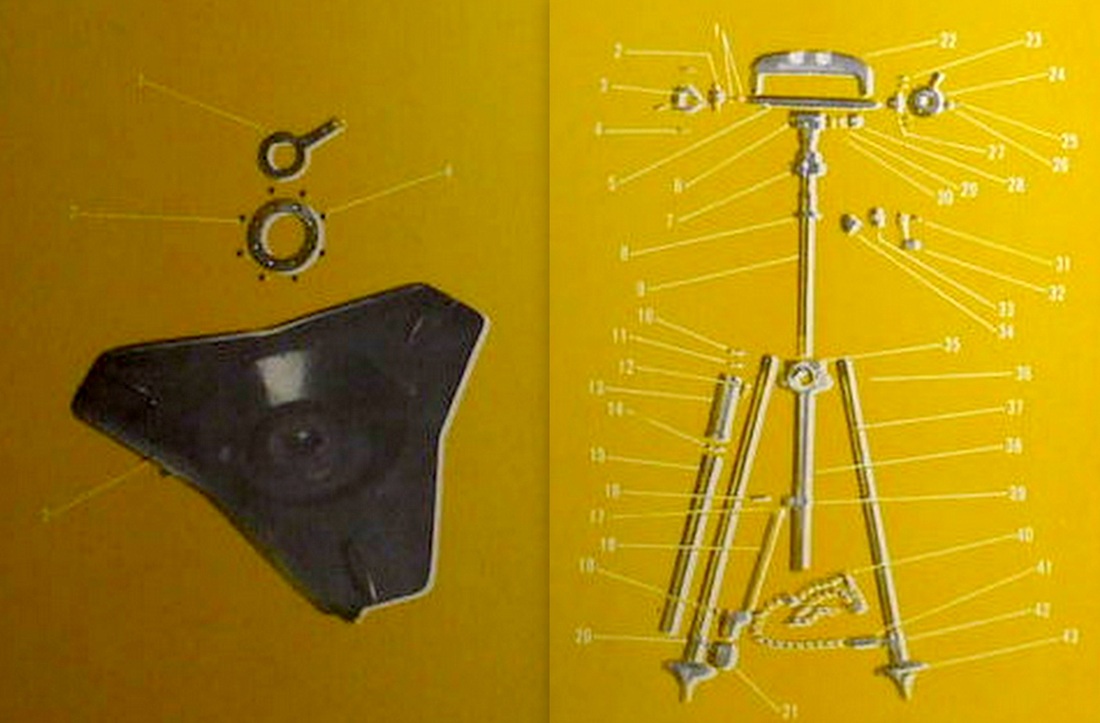
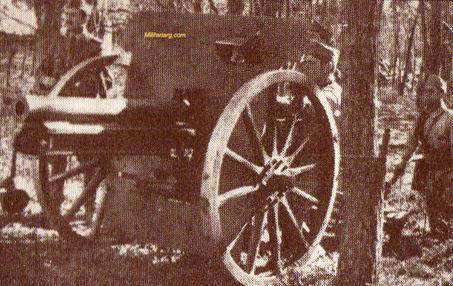
81 mm. Brandt Mortar.
An 81mm mortar, possibly a Stoker Brandt with illuminating type shell. The mortar designed by Edgar Brandt became a model for many countries, including the US and Russia. The modern mortar continues to be based on this advanced model.
1940s. Photo: UPI/AP
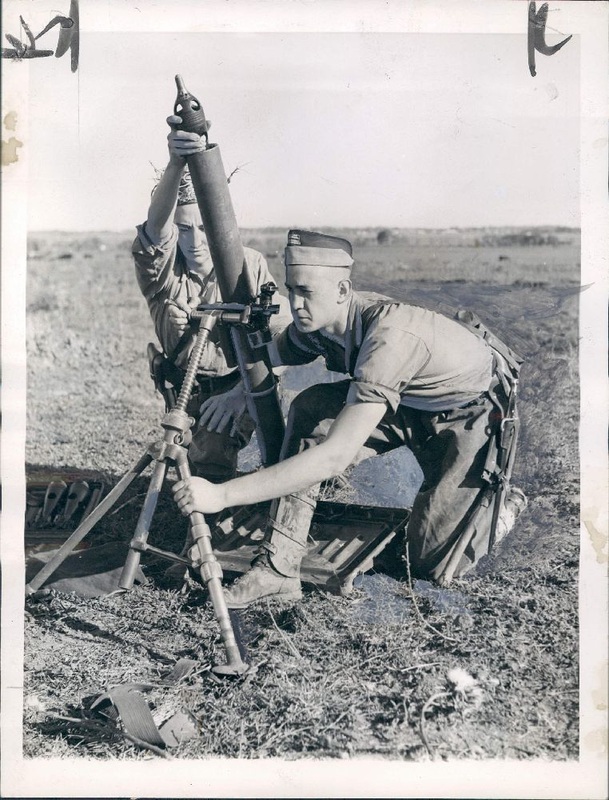
81mm mortar, type Brandt. 6th Regiment Infantry of Mercedes (1939)
DGFM 81 mm M1 type mortar w/ illuminating and high-explosive shell.
US M1 81mm Mortar and M1 Mount. The M1-81mm is the American version of the Stokes-Brandt.
1st Infantry Patricios Regiment.
81,4mm FM Mortar.
120mm FM Mortar.
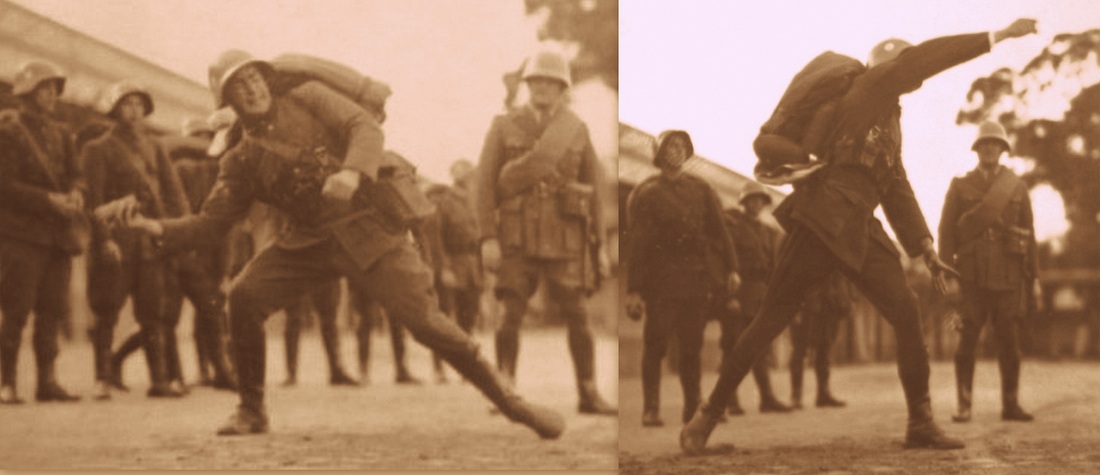
Anti-personnel Grenades
Argentine made Model 24 Stielhandgranate "Stick Grenades" and Hand Grenedes Lafitte, Bossone (?), FM-1, Oramil PO-1, FMK-1/FMK-2, Expal EA M-5, M67 fragmentation grenade and defensive smoke, etc .
Possibly training with offensive FM-1 grenades.
1946. 6th Infantry.
1936 Argentine Army Manual.
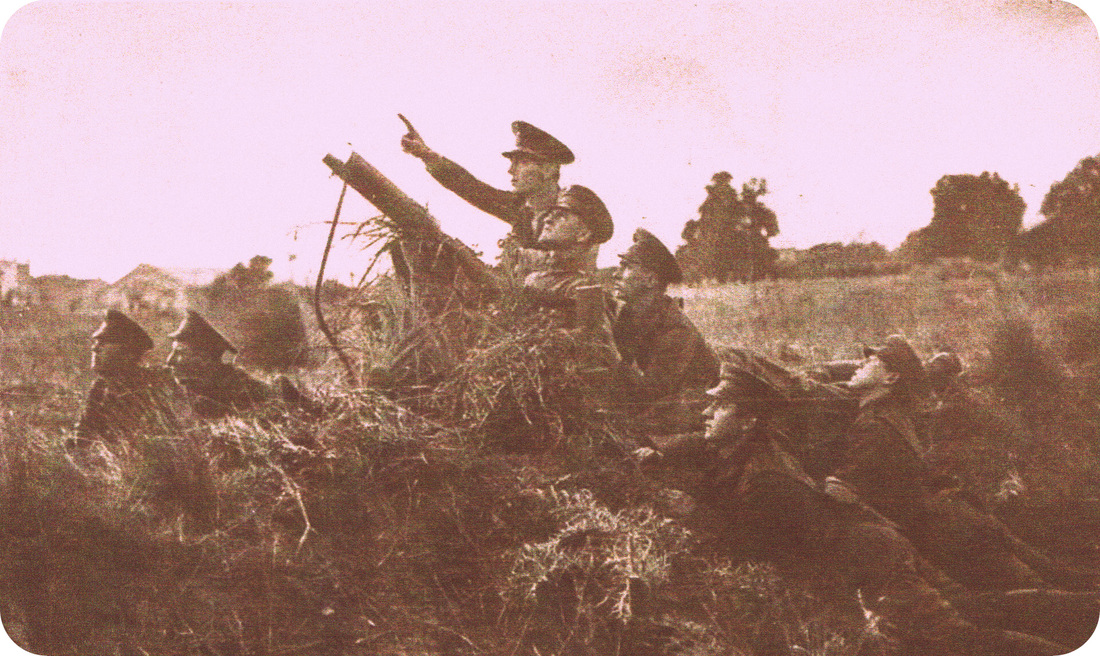
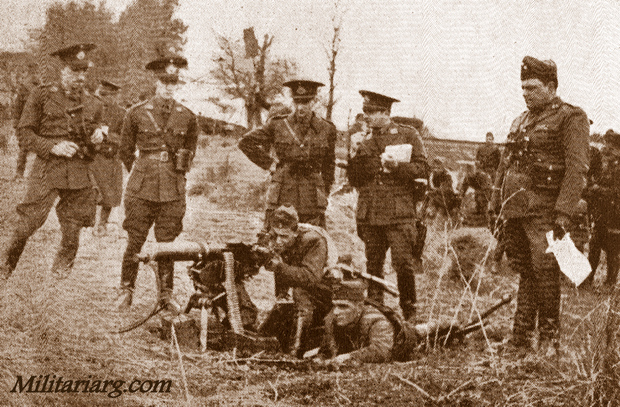
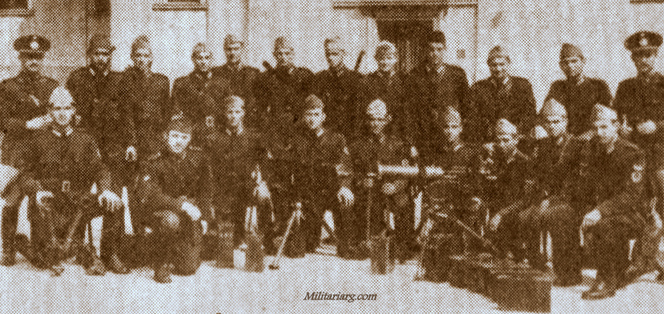
4th Infantry Regiment and School, 75mm Schneider ? and Maxim-Nordenflet Guns & Ammunitions Co Ld Machine Gun. Argentina had received the Gaitlings around 1870. At the end of the XIX century they may have received other machine gun Palmkrantz pattern like Nordenfelt and Berger & Co Maschinenfabrik Metallwarenfabrik/Rhur GmbH. Photos: Caras y Caretas 1933.
Section of Maxim-Nordenfelt machine gun in 1916. Caras y Caretas.
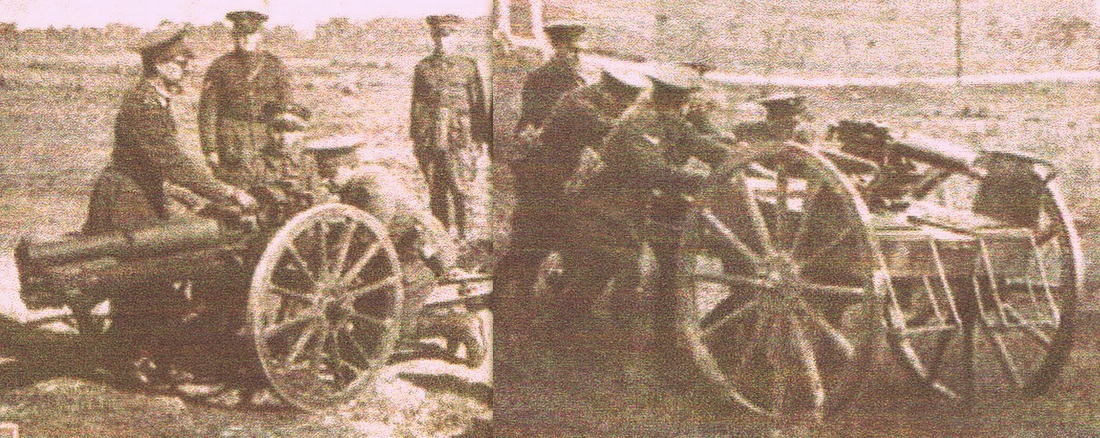
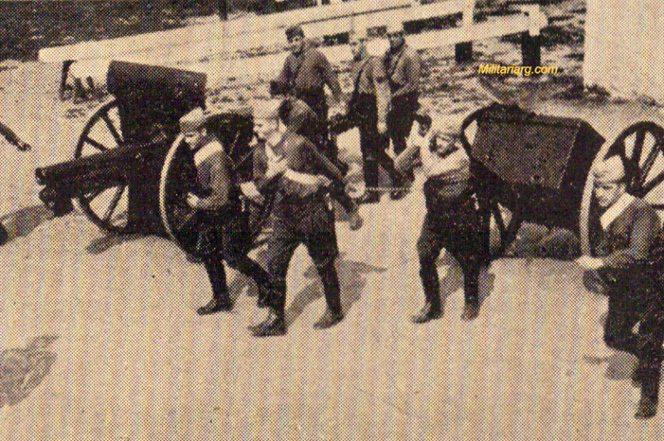
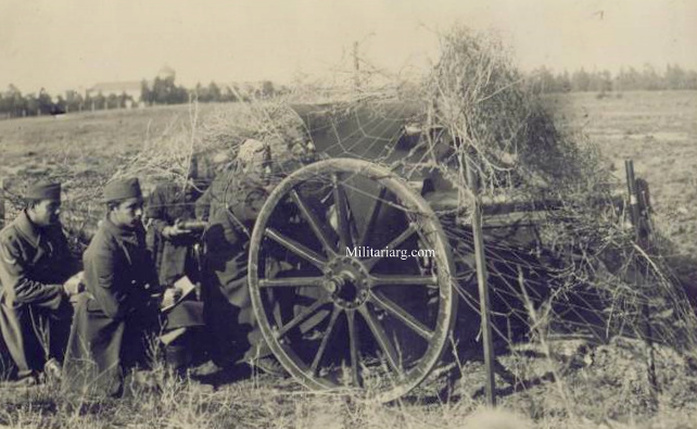
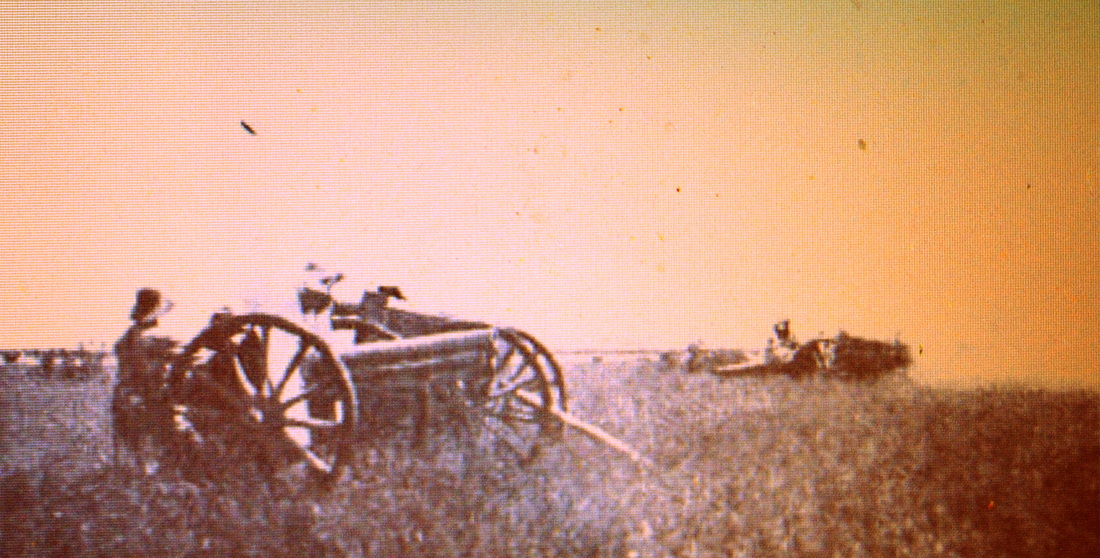
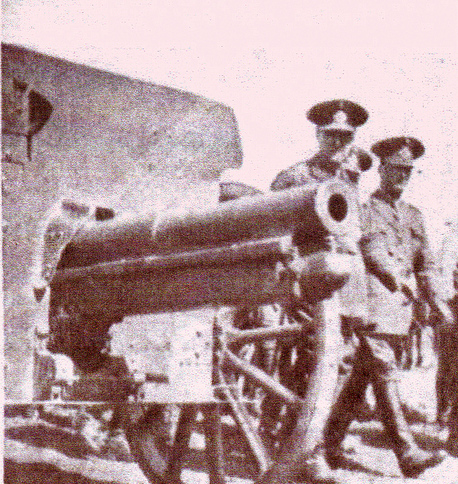
Campo de Mayo 1910. The General Van der Goltz was invited to attend the exercises. :eft: 75mm L28 M1898 (Krupp), Field Gun.
A battery of Krupp 75-mm cannons. Light or Assault Artillery, infantry support guns. Patricios Regiment, 1944.
Krupp 75mm “infantry guns,” ranging from 37mm to 75mm caliber.
1909 Krupp
75mm during maneuvers in Entre Rios. 1938, Caras y Caretas.
Water-cooled Heavy Machine Gun Colt-Browning M1917 (Argentine contract 1928). Patricios Regiment 1944.
6th Regiment Infantry of Mercedes (1939)
Madsen M1926/M48 Light Machine Gun (LMG). Patricios Regiment 1944.
Madsen machine gun, 7.65x53mm Mauser and rangefinder camera.
1944. 6th Infantry Regiment. Gral Viamonte. DGFM 81 mm Mortar
75mm L30 Krupp 1909.
1944. 6th Infantry Regiment. Gral Viamonte.
Gattling Machine-gun Model 1865.
Left: A Nordenfelt Gun multiple barrel machine gun? Right: 75mm Krupp. 1946. 6th Infantry Regiment. Gral Viamonte.
Flare Pistols & Signal Pistols
DGFM and HAFDASA. Source: "Las armas modernas de la infanteria by Julio Guzman. 1953"
1935. Photo: Caras y Caretas. Quick-firing gun.
"Matorras" 75mm. L.13 Mod. 1945. DGFM.
Above is a light gun that the infantry could carry on their own without the need for assistance from the organic divisional artillery. It is also an arm that could be used by mountain troops and paratroopers. The Matorras 75mm (7.5cm) was possibly based on the German 7.5cm Infantry Gun IG18. This gun was based on a barrel tube of an old 75mm (Krupp).
"Nedinsco, Carl Zeiss"
http://www.rubags.com/german-sniper-scope-nedinsco-carl-zeiss-kar-98-mauser.html
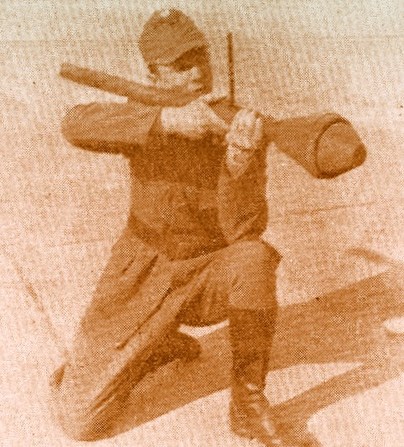
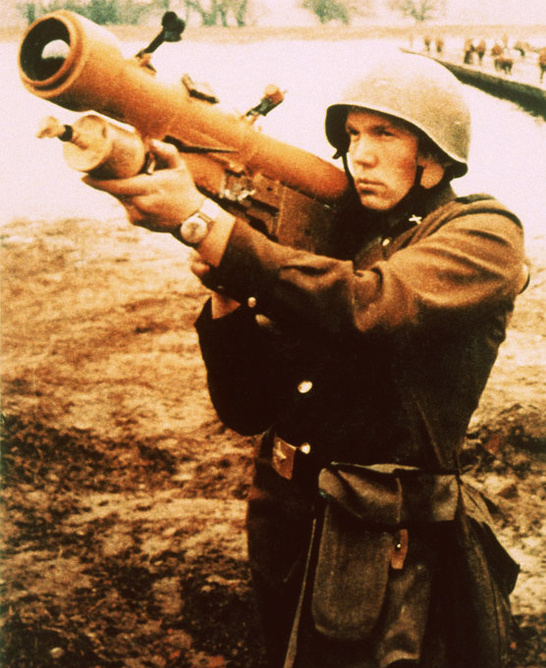
M9 and M9A1 2.36" Rocket Launcher (Bazooka)
DGFM Flamethrower
DGFM. Backpack-type flamethrower
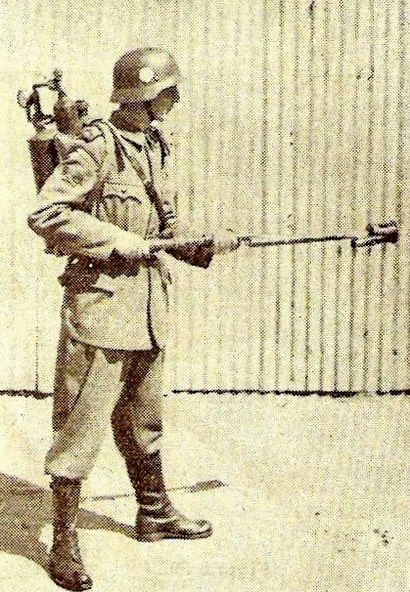
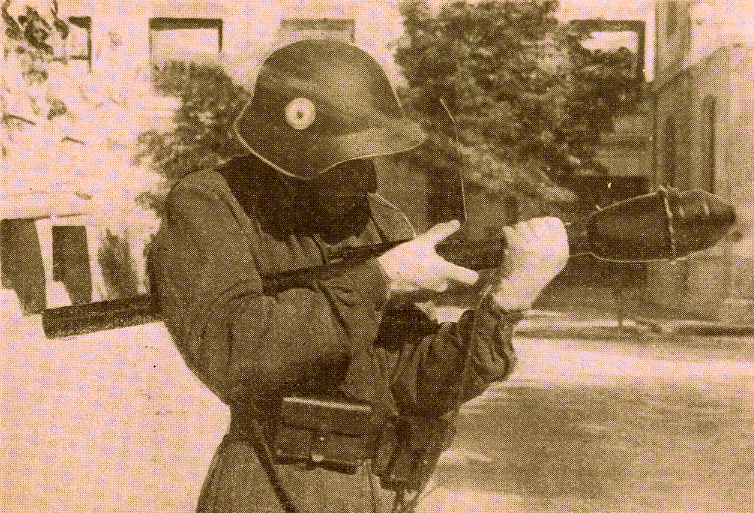
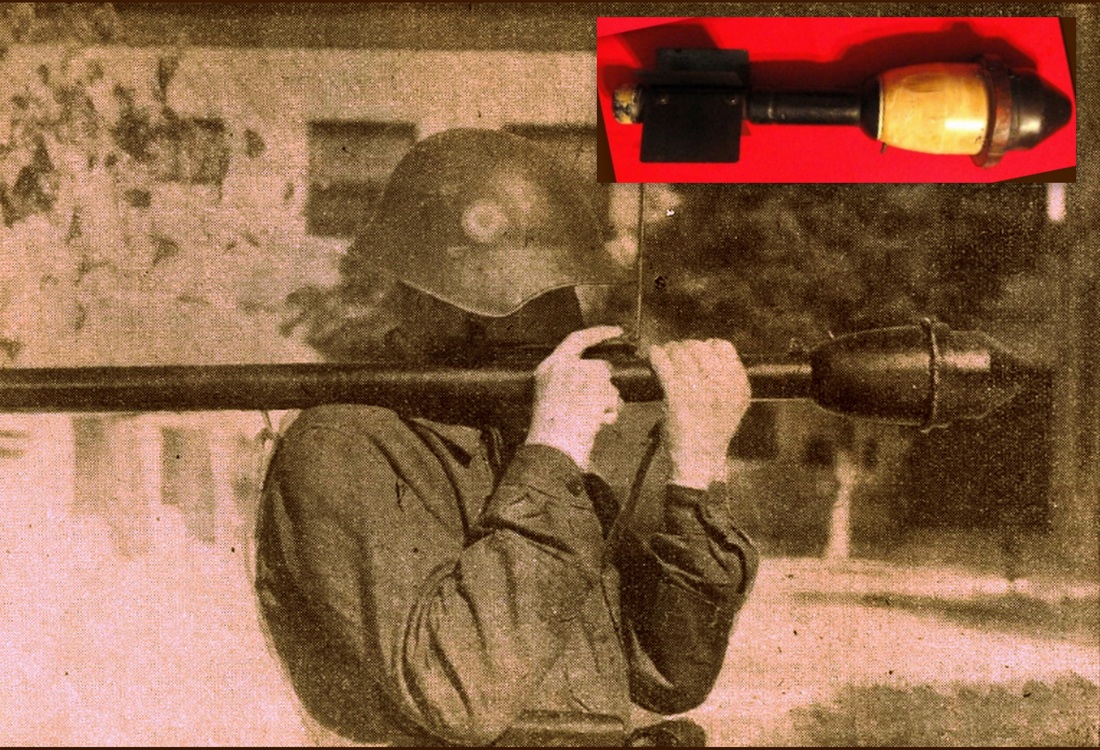
Rocket-propelled grenade
Panzer-Kott M46 Bofors.
P.A.P.I (Proyectil antitanque para infanteria), DGFM. Rocket-propelled grenade.
Source: Julio S. Guzmán, Las Armas Modernas de Infantería, Abril de 1953
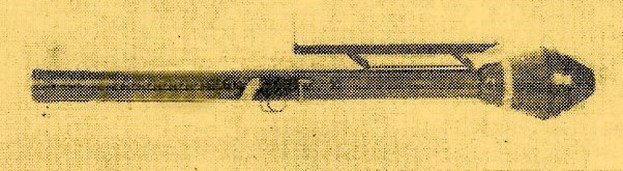
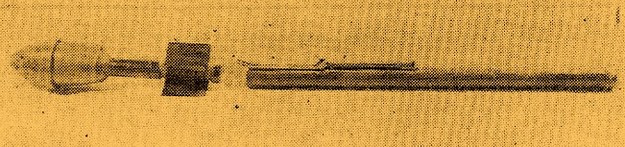
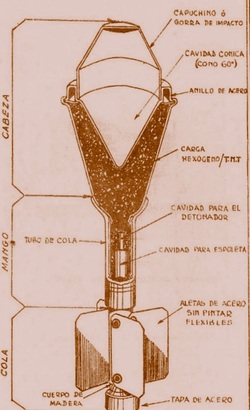
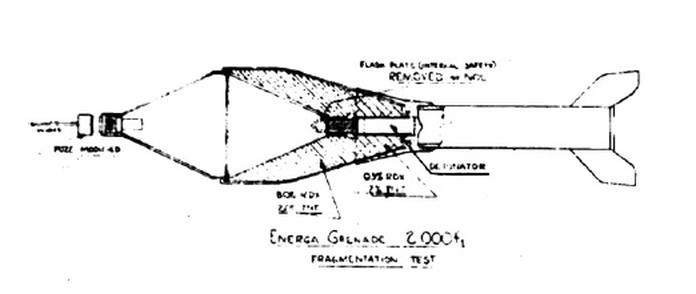
The Energa anti-tank rifle grenade is a rifle-launched anti-tank grenade that is propelled by a ballistite-filled blank cartridge. The name Energa comes from the firm in Liechtenstein that designed it, the Anstalt für die ENtwicklung von ERfindungen und Gewerblichen Anwendungen, based in Vaduz
P.D.E.F 40mm Double-Effect Fragmentation Projectile (Proyectil Doble Efecto de Fragmentación).
P.A.F 62mm Anti-Tank Fragmentation Projectile (Proyectil Antitanque de Fragmentación), Smoke, flares and ttaining (Blu), grenades.
Version of the hand grenade FMK2. It was projected from the mouth of the cannon of the 7.62mmx51 FAL with a special cartridge without a FMK-LGR projectile. The rifle has a "G" Grenade selector, in the gas-cylinder plug.
P.A.F 62mm Anti-Tank Fragmentation Projectile (Proyectil Antitanque de Fragmentación), Smoke, flares and ttaining (Blu), grenades.
Version of the hand grenade FMK2. It was projected from the mouth of the cannon of the 7.62mmx51 FAL with a special cartridge without a FMK-LGR projectile. The rifle has a "G" Grenade selector, in the gas-cylinder plug.
C3B AT Mine, (Spain). Argentina used a large variety of AT/AP mines from various origins, such Italian SB33 small metal blast AP, SB81 plastic cased AT, Spanish Anti-tank C3B and Anti-personnel P4B. Argentine DGFM: FMK1; FMK3 Fiberglass, FMK5 Metal Anti-Tank Blast Mine, Like the FMK-3 mine it uses a FMK-1 anti-personnel mine as a trigger. Israeli N4 AP and N6 AT,. US M1 Anti-Tank. Like on many other battlegrounds, the remaining mines in Malvinas are still a very real problem. During the war it is possible that the Royal Air Force used the BL755 cluster bomb on the minefields for breaching and cleaning.
Mine detectors: AN/PSS-11 (?); AN-19/2 Austrian Schiebel, (AN/PS-12). Before 1980s, the technology was new to Argentina. In the 1940s, gardening tools and techniques were the norm to remove mines as well as knives and bayonets. They also used old broom handles with nails at the end. The mine detector (Polish Mark-I), was an invention of Polish lieutenant Jozef Kosacki. His design was used by the British at El Alamein.
Soviet/Warsaw Pact weapons used by the Argentine Forces
Name: 9K32 Strela-2
NATO reporting name: SA-7 Grail
Type :Man portable surface-to-air missile launcher
Place of origin Soviet Union
NATO reporting name: SA-7 Grail
Type :Man portable surface-to-air missile launcher
Place of origin Soviet Union
Cold War-era propaganda. Soviet SA-7 Grail surface-to-air missile.
The 9K32 “Strela-2” (Russian 9К32 “Cтрела-2” — arrow; NATO reporting name SA-7 Grail) is a man-portable, shoulder-fired, low-altitude surface-to-air missile system with a high explosive warhead and passive infrared homing guidance. Broadly comparable to the US Army FIM-43 Redeye, it was the first generation of Soviet man portable SAMs, entering service in 1968, with series production starting in 1970.
Described by one expert as being "the premier Russian export line",the Strela and its variants have seen widespread use in nearly every regional conflict since 1968.
During Malvinas War:
A handful of missiles were fired, but no kills were scored. War Machine Encyclopedia gives no launch recorded, but several missiles were captured, probably they came from Libya. (Actually they came from Perú)
The 9K32 “Strela-2” (Russian 9К32 “Cтрела-2” — arrow; NATO reporting name SA-7 Grail) is a man-portable, shoulder-fired, low-altitude surface-to-air missile system with a high explosive warhead and passive infrared homing guidance. Broadly comparable to the US Army FIM-43 Redeye, it was the first generation of Soviet man portable SAMs, entering service in 1968, with series production starting in 1970.
Described by one expert as being "the premier Russian export line",the Strela and its variants have seen widespread use in nearly every regional conflict since 1968.
During Malvinas War:
A handful of missiles were fired, but no kills were scored. War Machine Encyclopedia gives no launch recorded, but several missiles were captured, probably they came from Libya. (Actually they came from Perú)
KBM Kolomna 9K32 Strela-2 missile and canister
Source: Wikipedia
Source: Wikipedia
Malvinas Campaign
M20A1/A1B1 "Super Bazooka".
Instalazas 88.9mm M-65.
The 25th Infantry Regiment (RI 25) is a unit of the Argentine Army based at Sarmiento, Chubut, Argentina. This regiment fought during Malvinas War. He wore the FMK1 Hand Grenades. Argentina also used the FMK 2 GME, M67 fragmentation hand grenade, M16 Smoke Hand Grenade, EXPAL EA M-5, US M69.