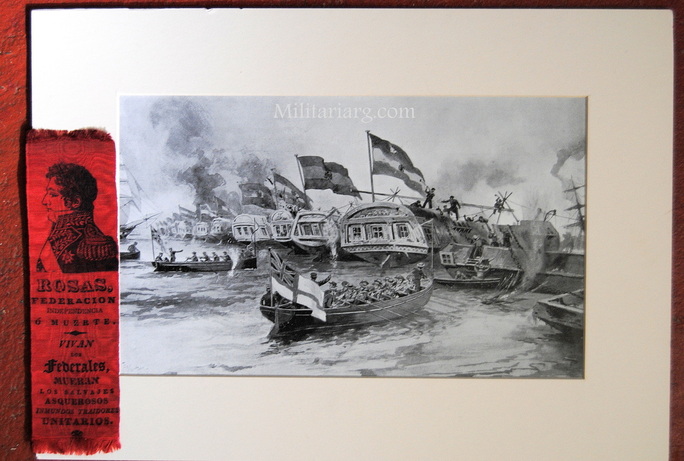
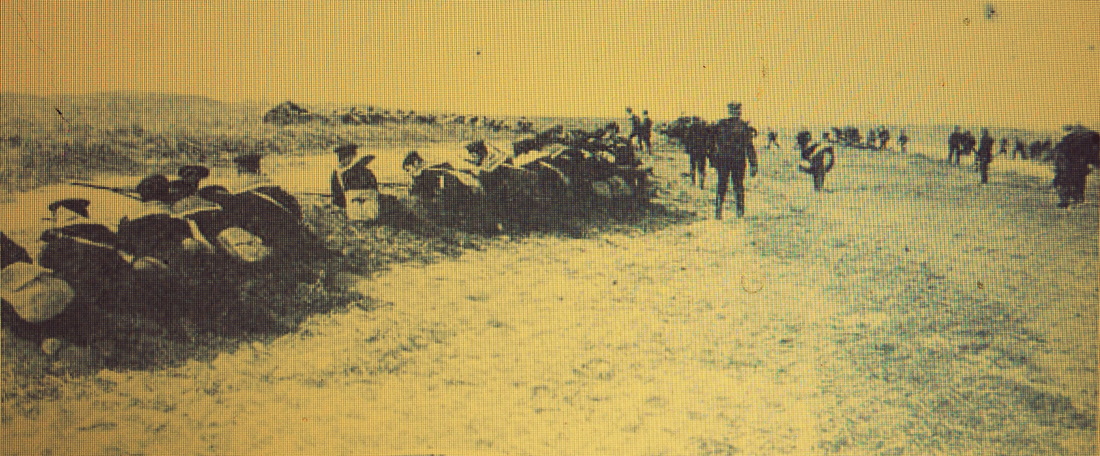
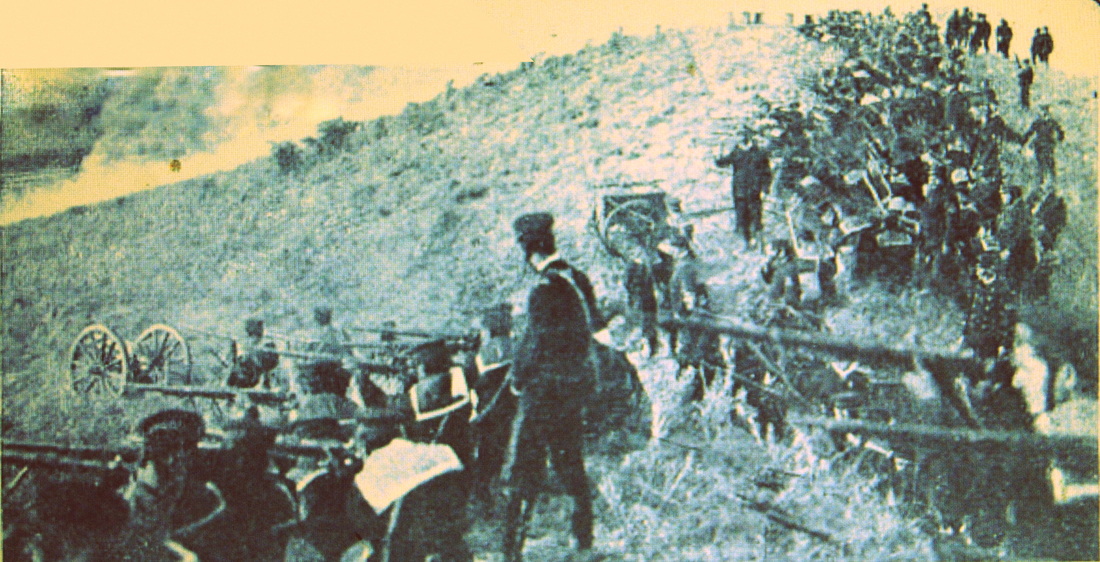
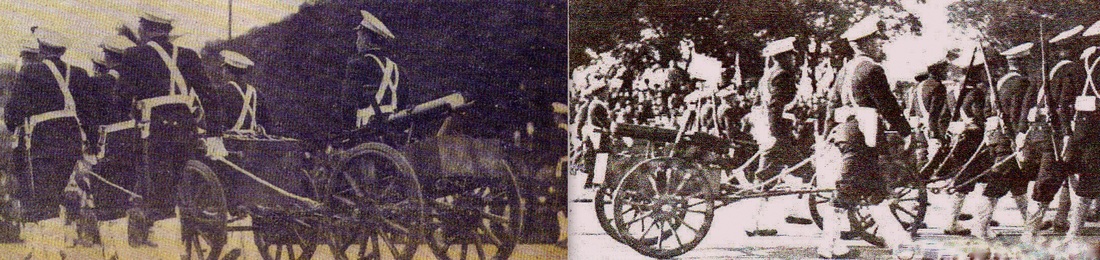A original print of The Navy and the men of The Firebrand cutting he booms of The Argentine Navy during The Battle of Obligado in 1845. On the side is a red ribbon that was found inside of a Bible which was placed there by a German priest who had been in Buenos Aires and then returned to Germany.
Below is the transcription from the back of the picture:
"In 1845 The British and French squadrons in South America were ordered to reopen The Parana River, which had been closed by Rosas, President of Argentine Republic. Rosas had taken a strong position at Obligado, commanded by four batteries, with a boom, composed of vessels moored and connected by chains, acros the river, and a ship of war and some gun-boats above this defence. The british force consisted of six vessels (Two paddle steamers), and the French of five vessels, (One paddle steamer); and on the 20th November they advanced to cut the boom and capture the forts. The wind was light, and the sailing vessels were severely handled by the batteries in detail, being unable to carry out the programme and act in concert. Soon after noon Captain James Hope, of The "Firebrand" volunteered to cut the boom. Taking with three boats, with armourers, and assisted by Liutenant Webb, Mr. Nicholson (mate), and mr Commerell (midshipman), he accomplished his purpose in four minutes, under a tremendous fire.
Below is the transcription from the back of the picture:
"In 1845 The British and French squadrons in South America were ordered to reopen The Parana River, which had been closed by Rosas, President of Argentine Republic. Rosas had taken a strong position at Obligado, commanded by four batteries, with a boom, composed of vessels moored and connected by chains, acros the river, and a ship of war and some gun-boats above this defence. The british force consisted of six vessels (Two paddle steamers), and the French of five vessels, (One paddle steamer); and on the 20th November they advanced to cut the boom and capture the forts. The wind was light, and the sailing vessels were severely handled by the batteries in detail, being unable to carry out the programme and act in concert. Soon after noon Captain James Hope, of The "Firebrand" volunteered to cut the boom. Taking with three boats, with armourers, and assisted by Liutenant Webb, Mr. Nicholson (mate), and mr Commerell (midshipman), he accomplished his purpose in four minutes, under a tremendous fire.
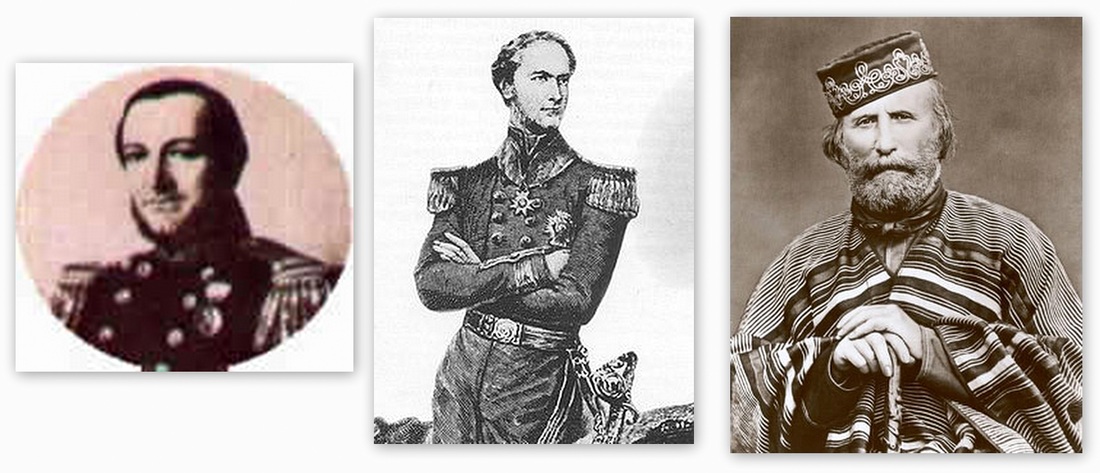
Lef: Admiral Louis Leblanc. Center: Admiral Sir Charles Hotham. Right: Giuseppe Garibaldi.
One of the first actions of the Marines could go back to combat in 1842 Costa Brava, where the Argentina Confederation fleet under William Browm defeated Giuseppe Garibaldi after two days of naval and coastal fighting. The
confederation's coastal artillery Argentina from 1845 to 50 had a conflict with French and British fleet commanded by the admirals Massieu de Clerval and Sir Charles Hotham. Although much earlier, during the war between France and
Argentina Confederation in 1838, the French in command of Lieutenant Commander Daguenet under orders of Admiral Louis Leblanc Martin Garcia island take the heroically defended by Colonel Jeronimo Costa Patricios Regiment commanded. The defenders surrendered and were greeted with honors from the French.
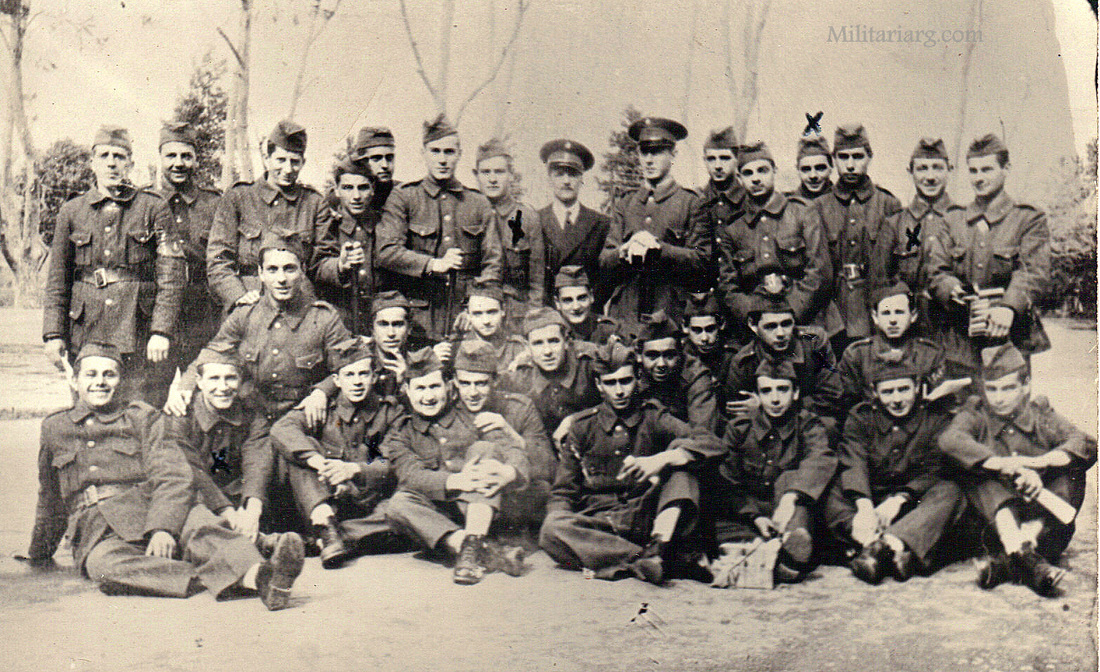
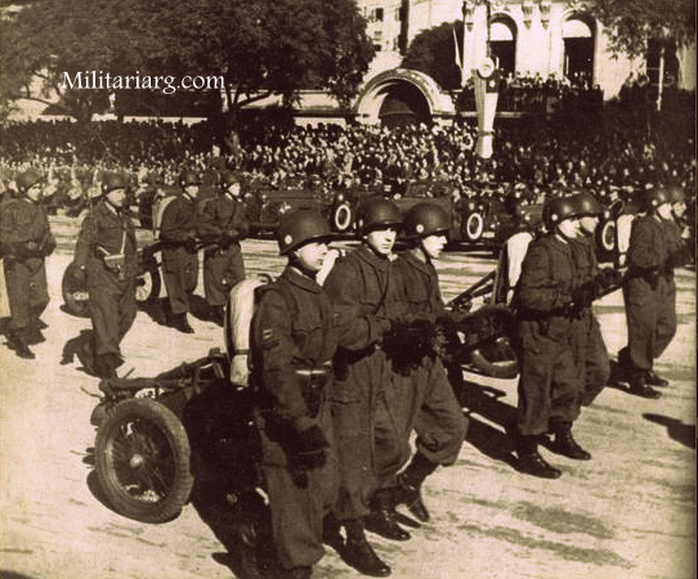
In 1938 The Coastal Artillery became known as (Infanteria Marina) Marines.
One of the first actions of the Marines could go back to combat in 1842 Costa Brava, where the Argentina Confederation fleet under William Browm defeated Giuseppe Garibaldi after two days of naval and coastal fighting. The
confederation's coastal artillery Argentina from 1845 to 50 had a conflict with French and British fleet commanded by the admirals Massieu de Clerval and Sir Charles Hotham. Although much earlier, during the war between France and
Argentina Confederation in 1838, the French in command of Lieutenant Commander Daguenet under orders of Admiral Louis Leblanc Martin Garcia island take the heroically defended by Colonel Jeronimo Costa Patricios Regiment commanded. The defenders surrendered and were greeted with honors from the French.
In 1938 The Coastal Artillery became known as (Infanteria Marina) Marines.
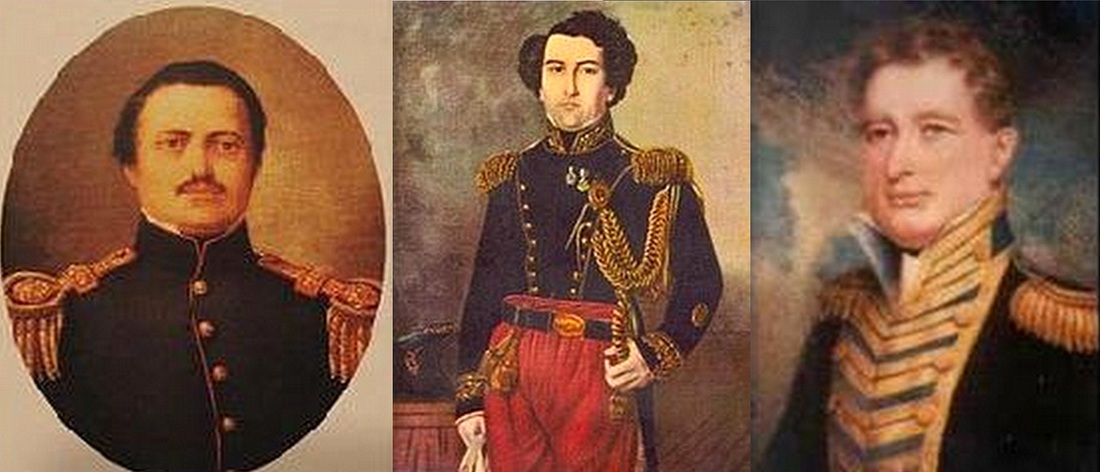
Left: Cnel Jeronimo Costa. Center: General Lucio Mansilla. Right: Admiral Brown.
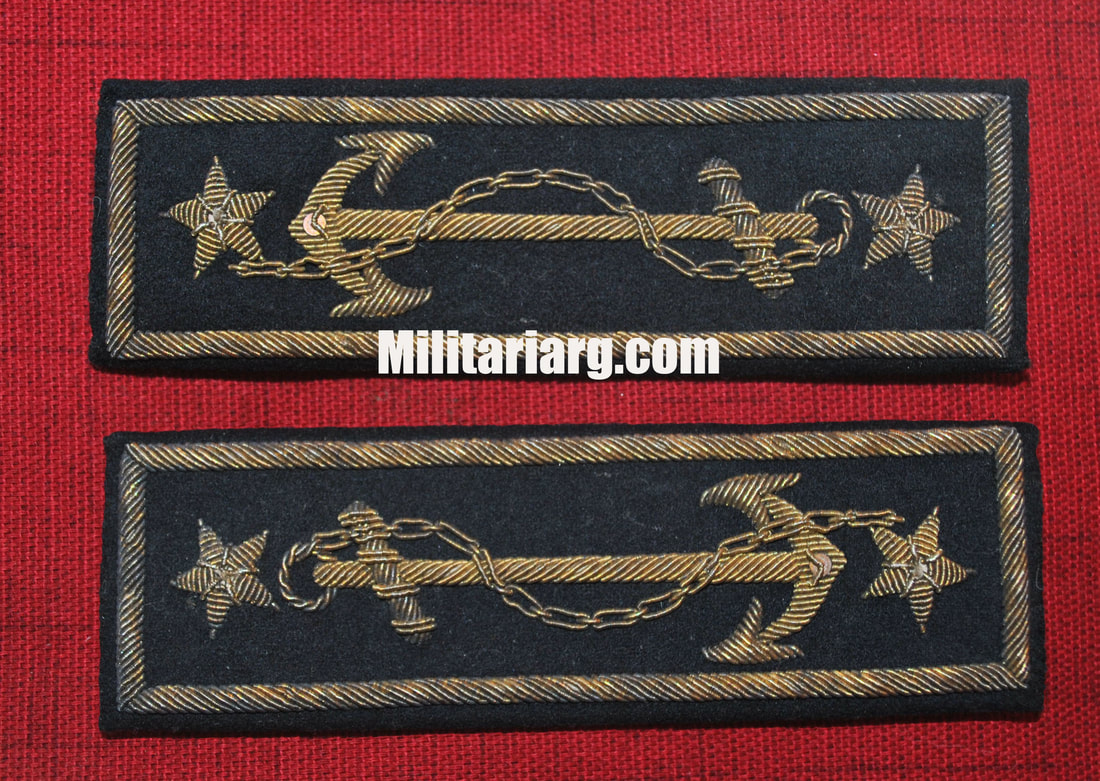
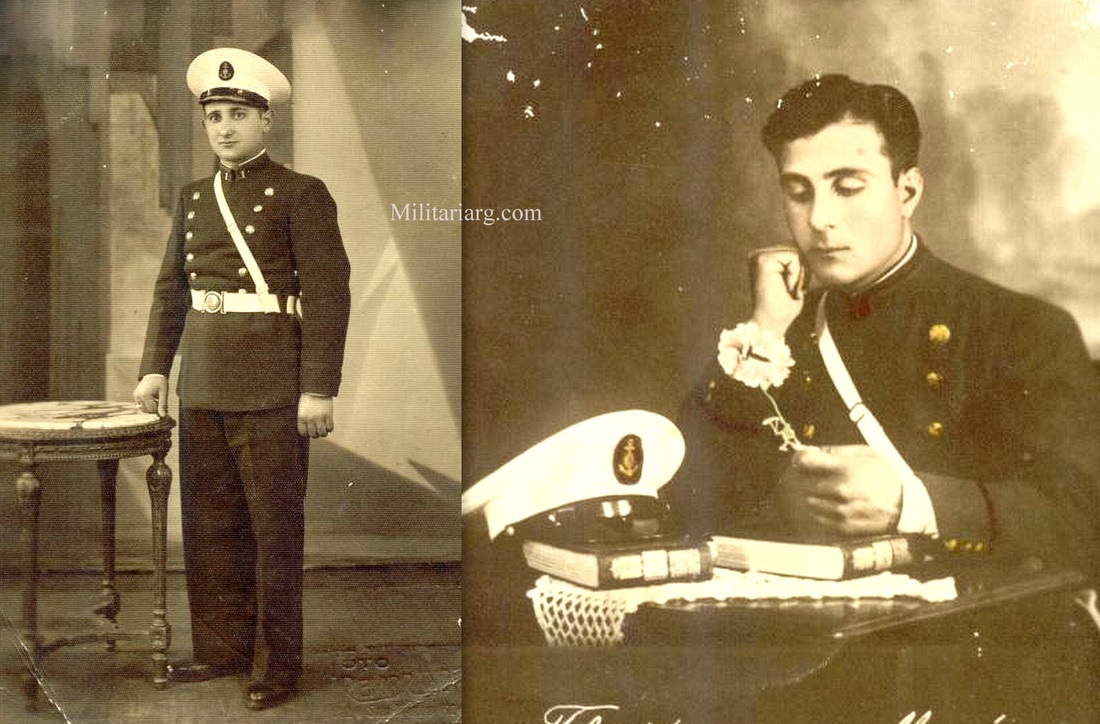
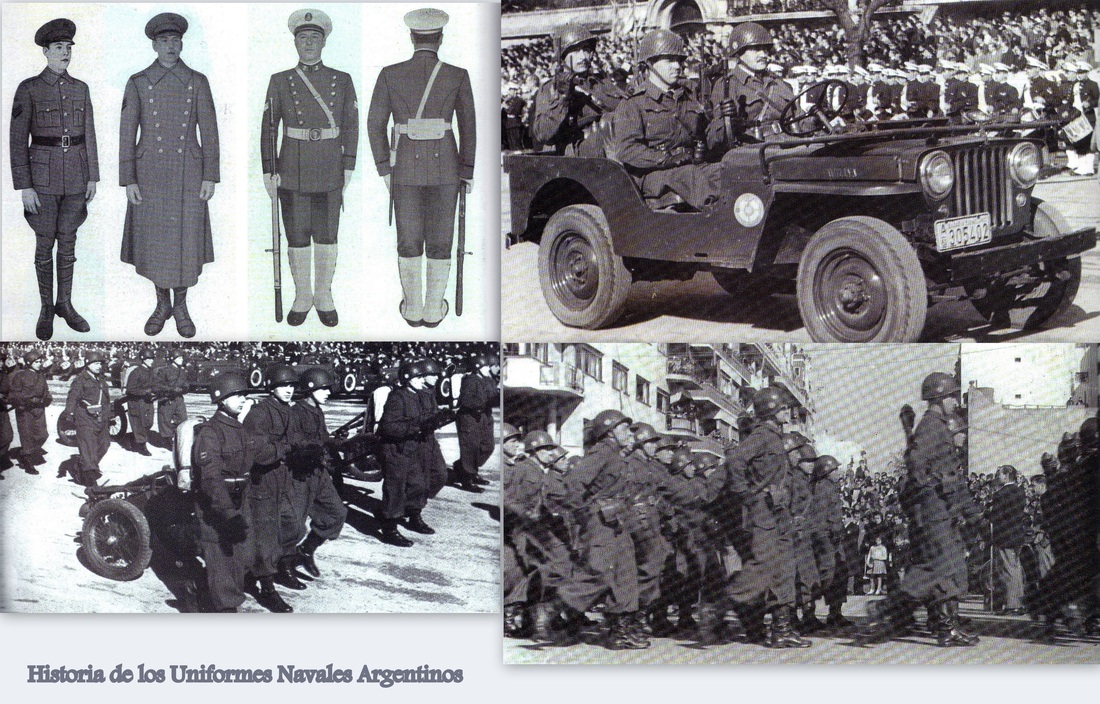
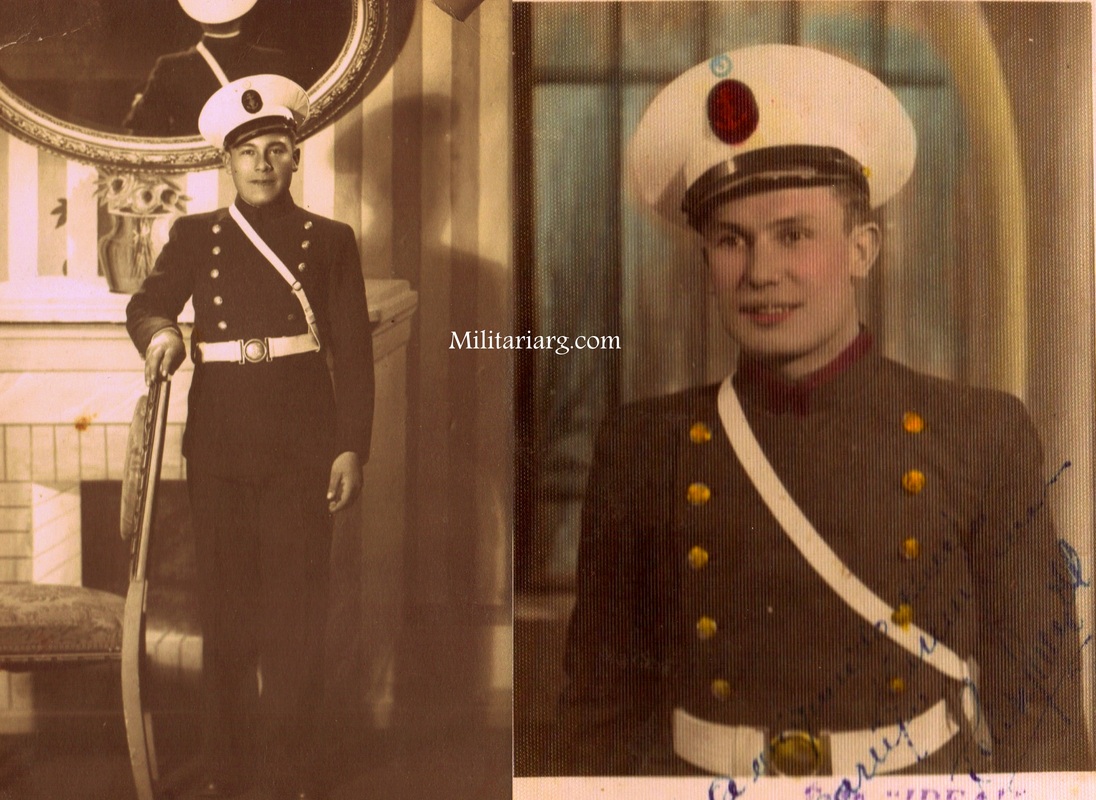
Model 1901 Argentine Navy shoulder boards loops, "Ship-of-the-line".
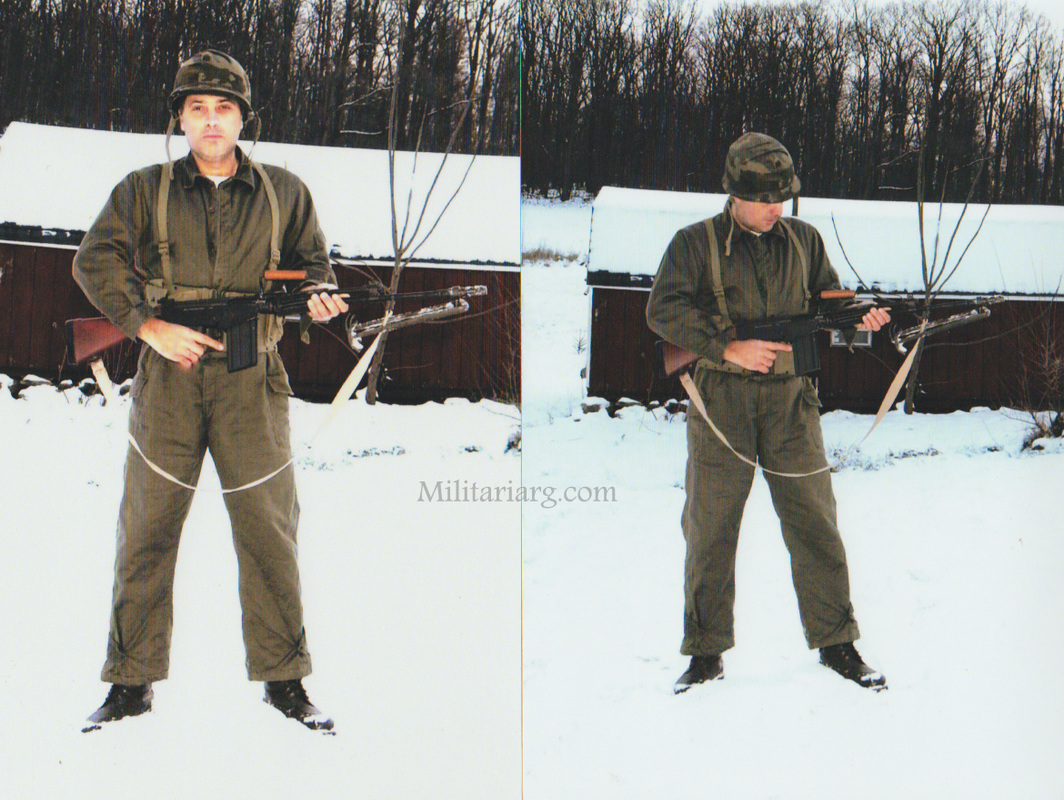
1901 Uniform. Gew88 1888 Commission Rifles?
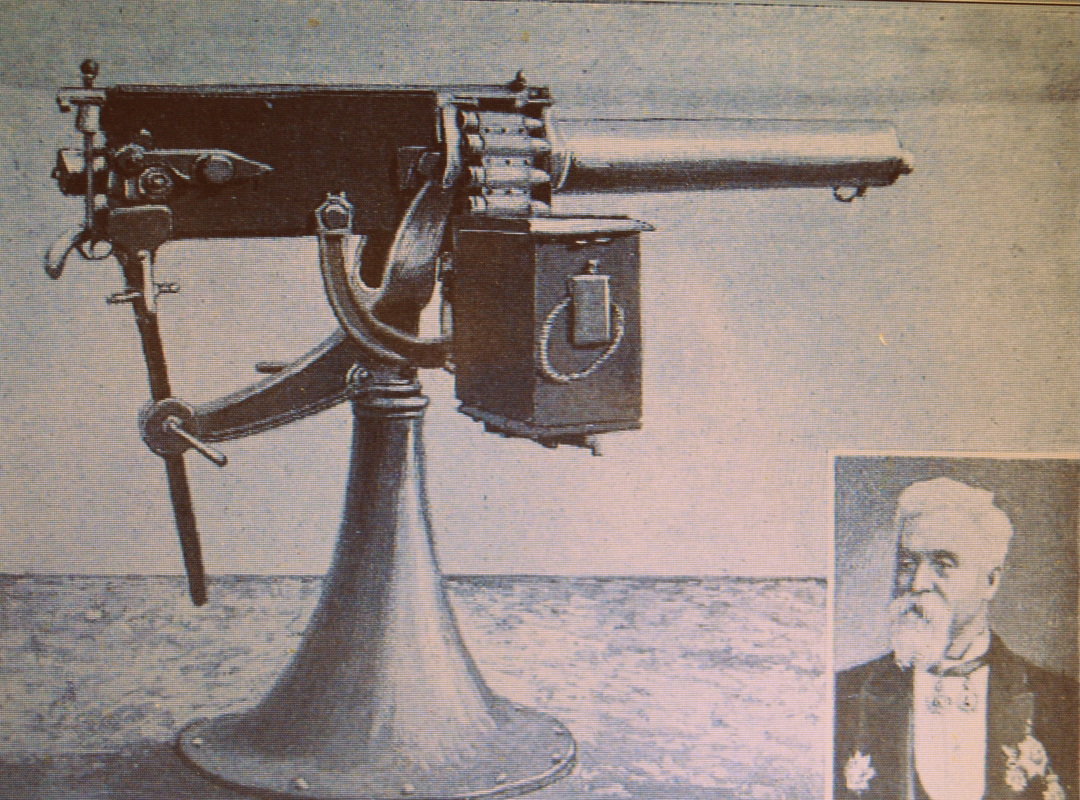
In 1888 the "Nordenfeldt Guns and Ammunition Co." became the "Maxim Nordenfeldt Guns and Ammunition Co." In the photo is Hiram Maxim. Helge Palmcrantz developed his machine gun in 1873 in association with the banker Thorsten Nordenfelt, both Swedish.
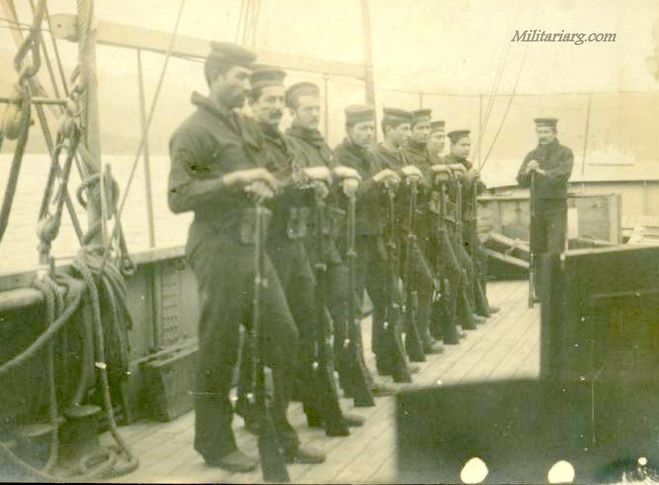
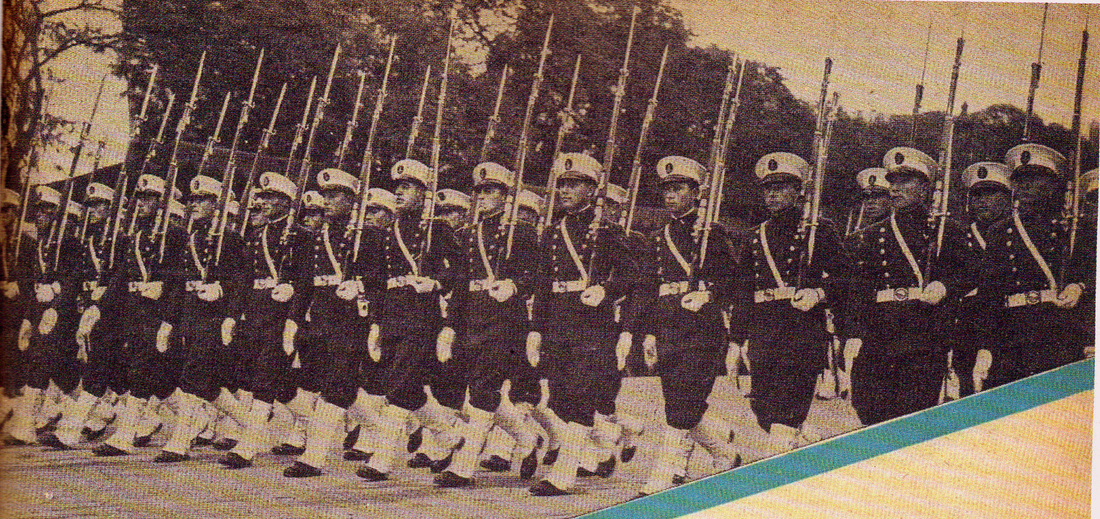
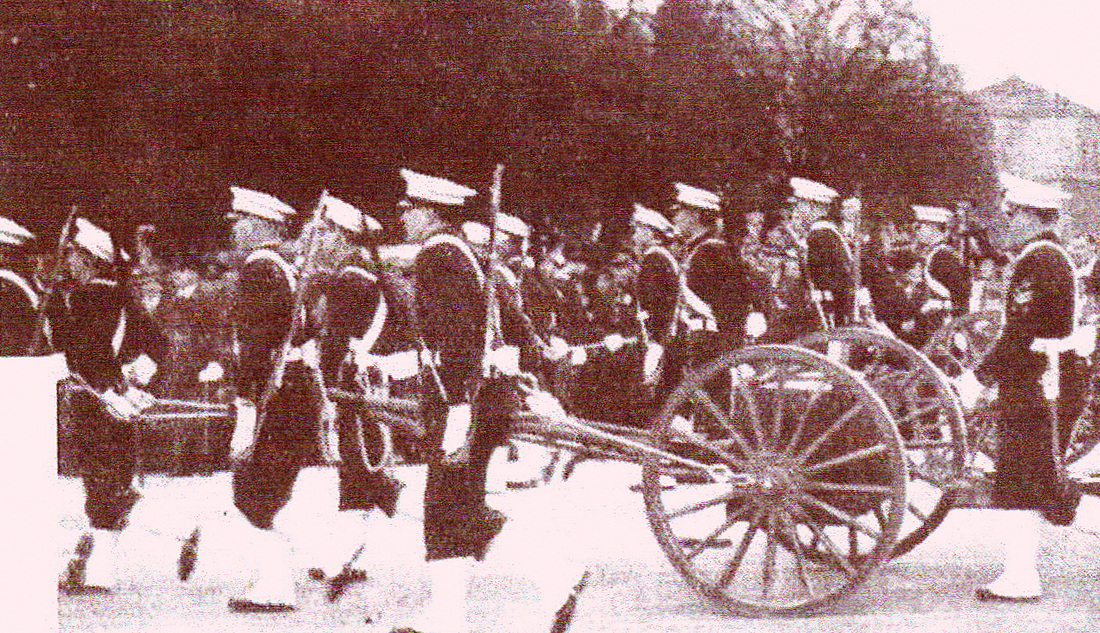
Uniform Model 1901. Very old photo of the coastal artillery. Observe the early Maxim 1884 on the gun field carriage and the armor bullet proof shield.
Caras y Caretas Magazine.
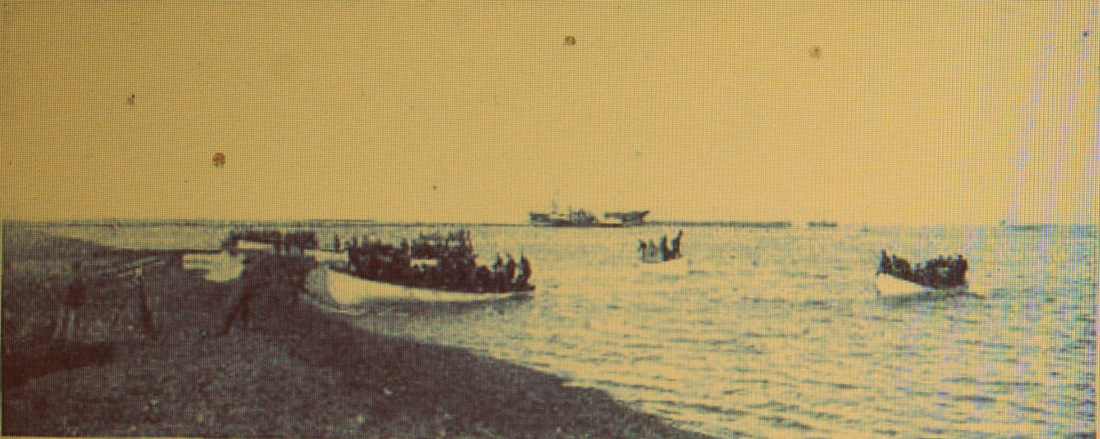
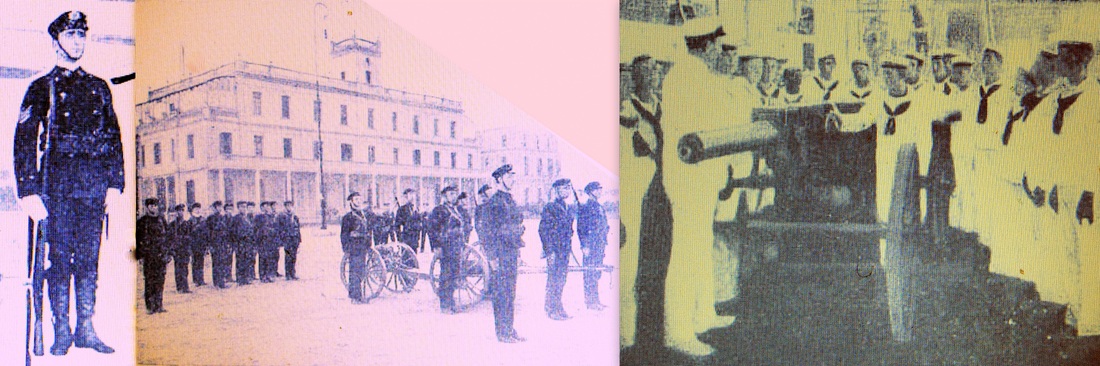
Avisos "Tehuelche" and "Fueguino" which are being used as transport for coastal artillery troops. Caras y Caretas 1902.
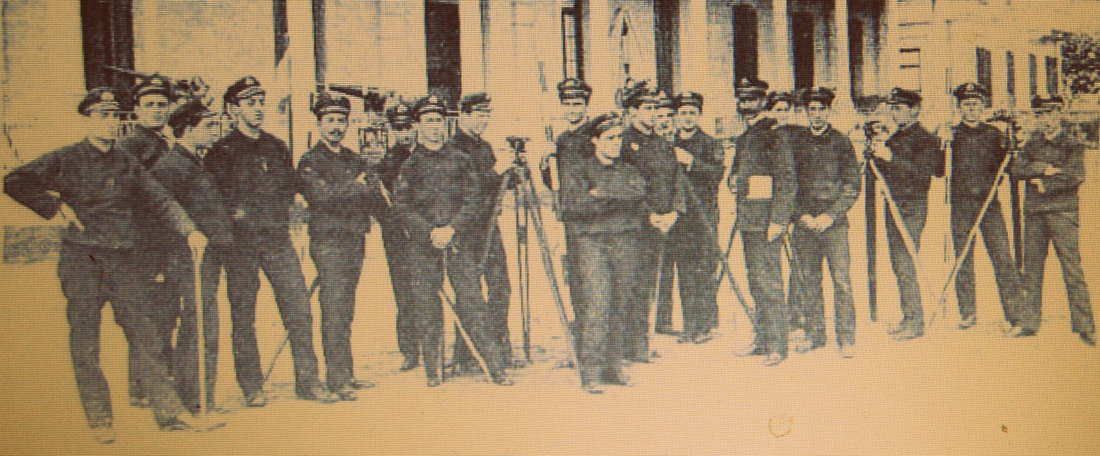
1903, instruction with Mauser M1991. Caras y Caretas.
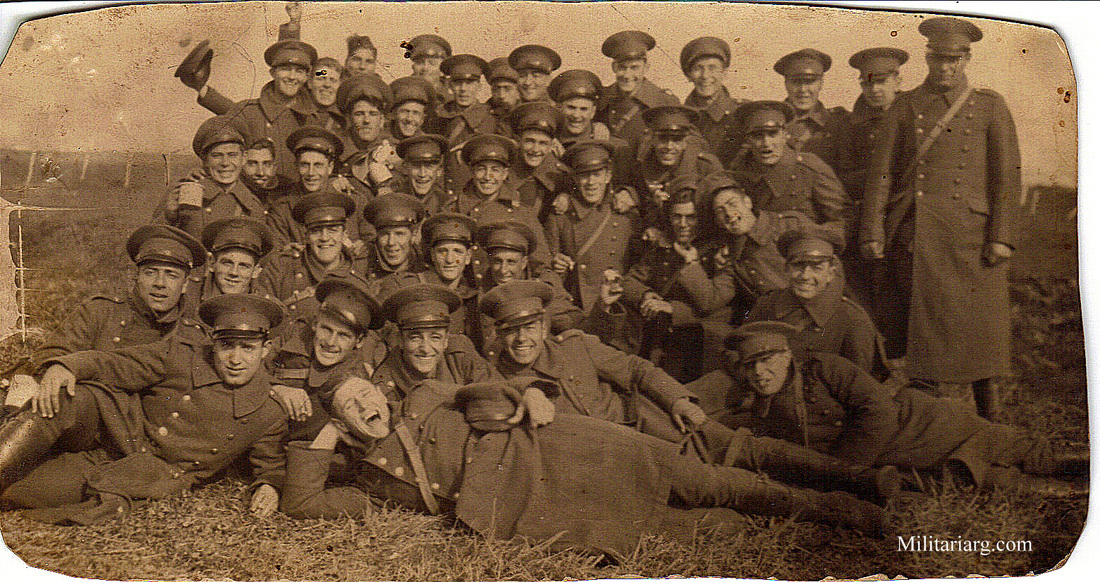
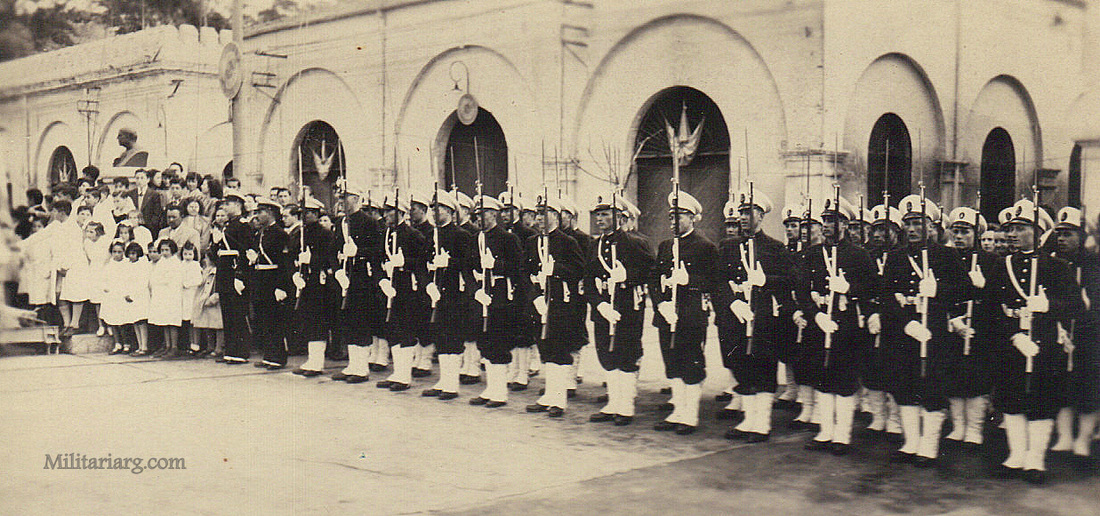
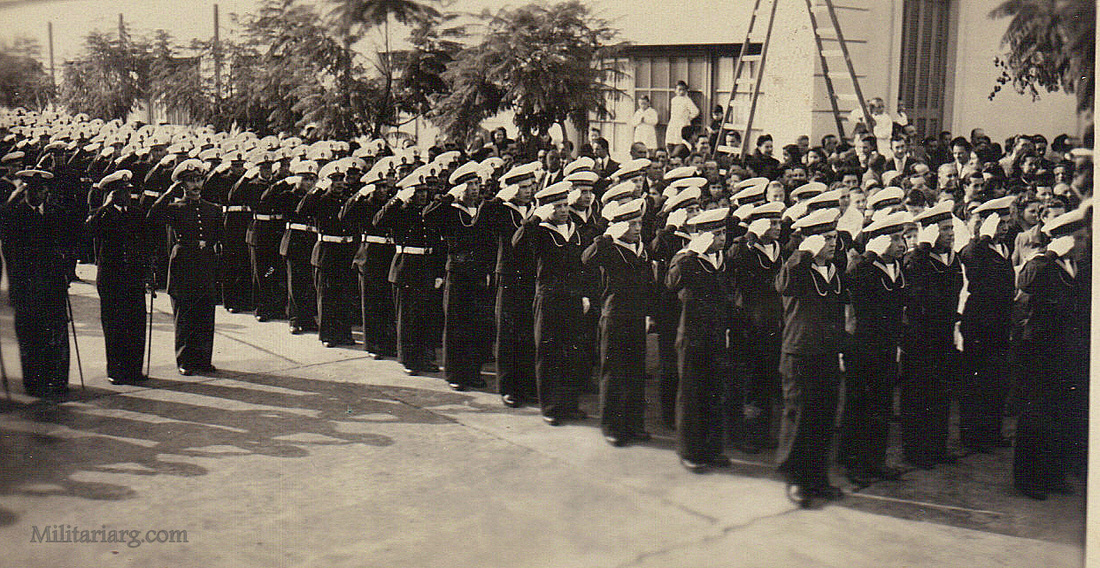
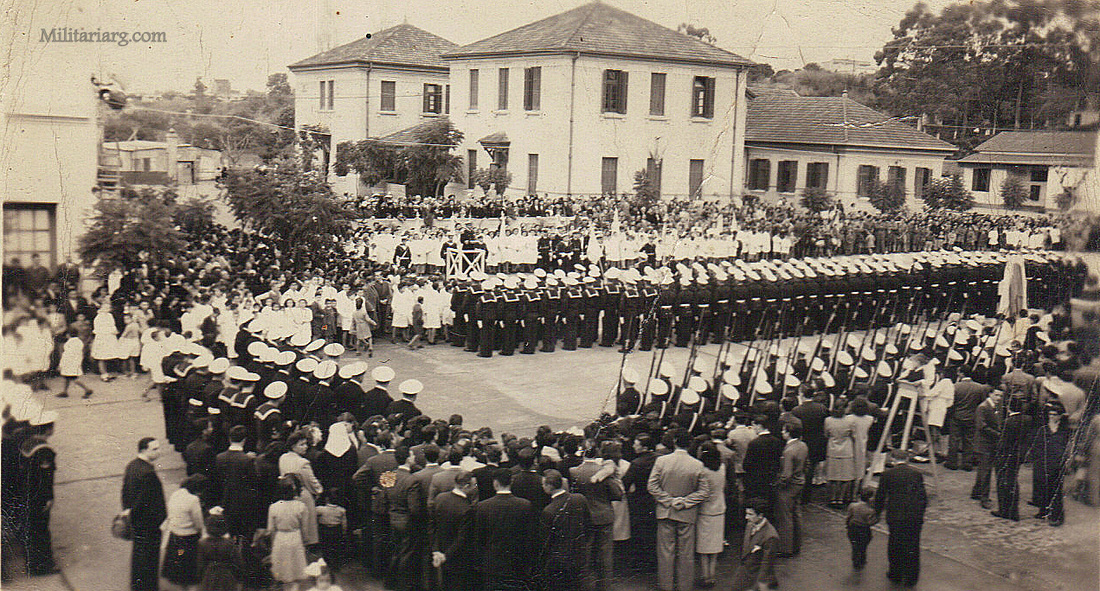
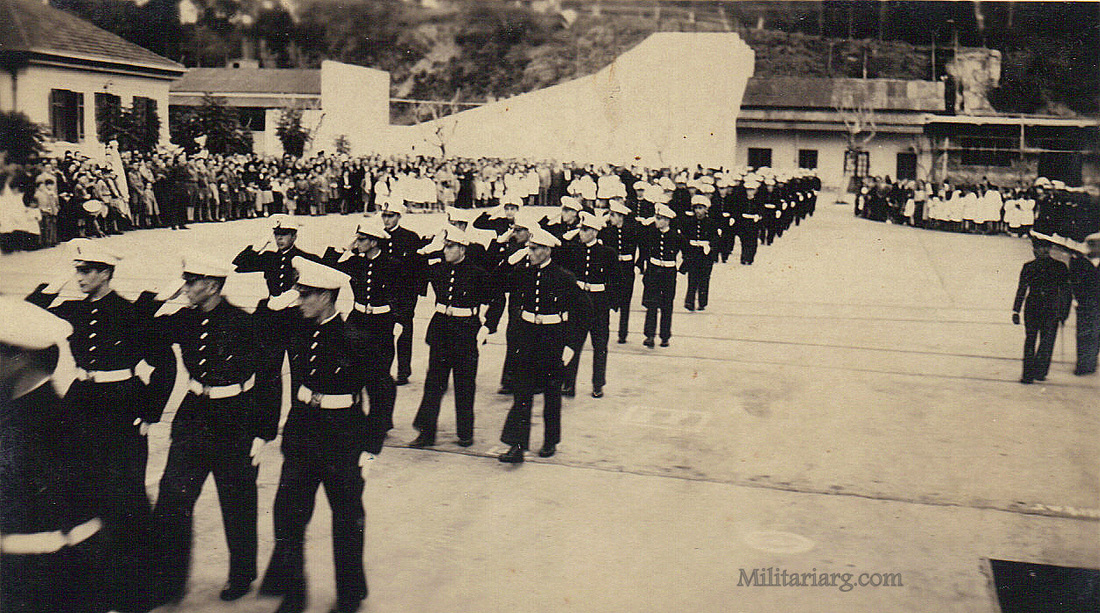
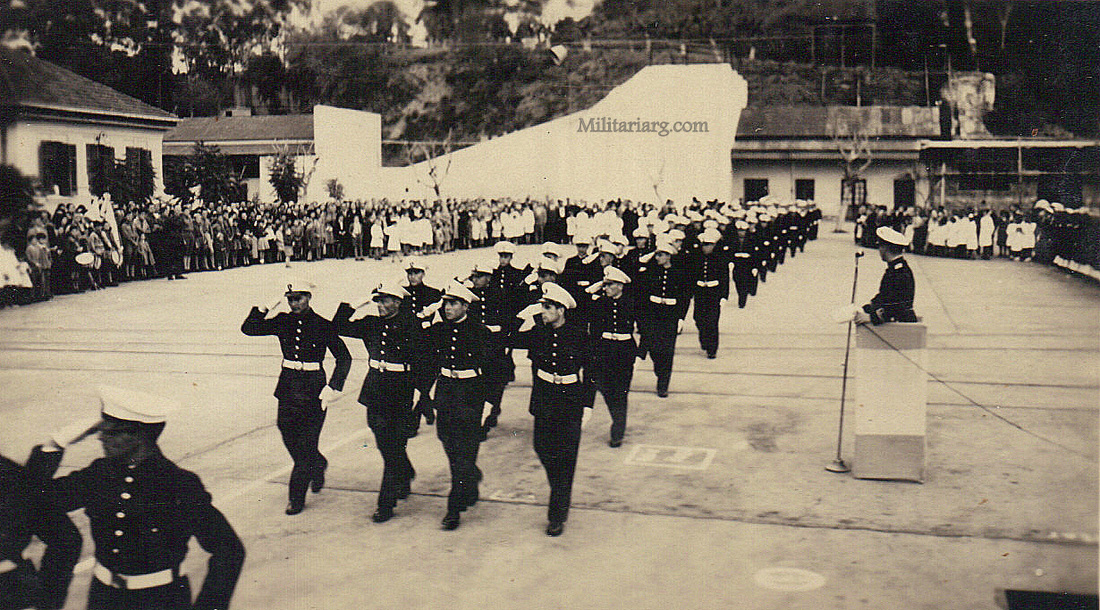
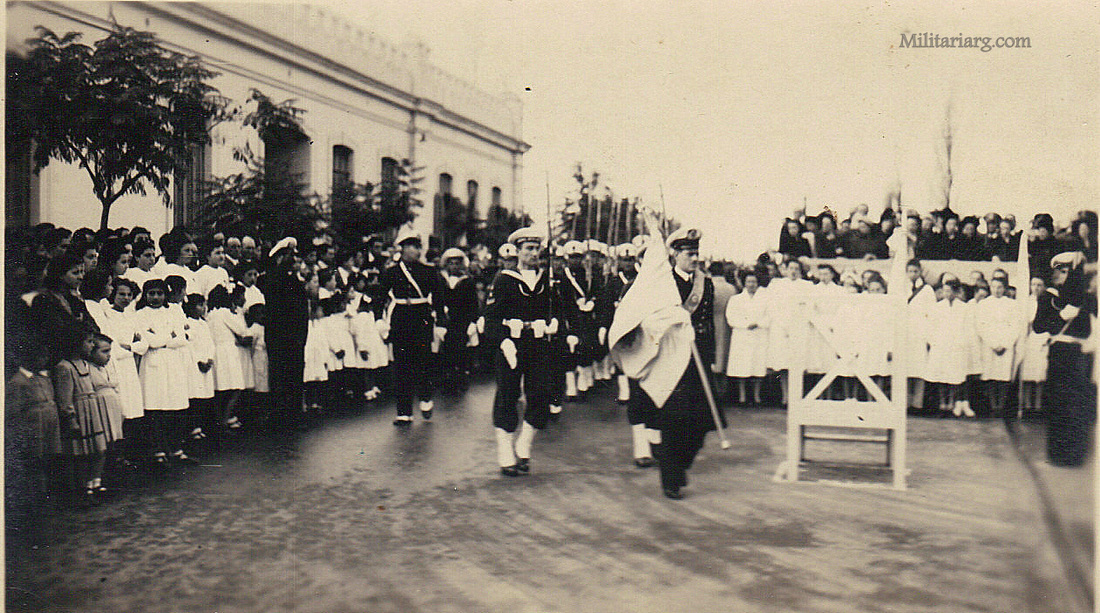
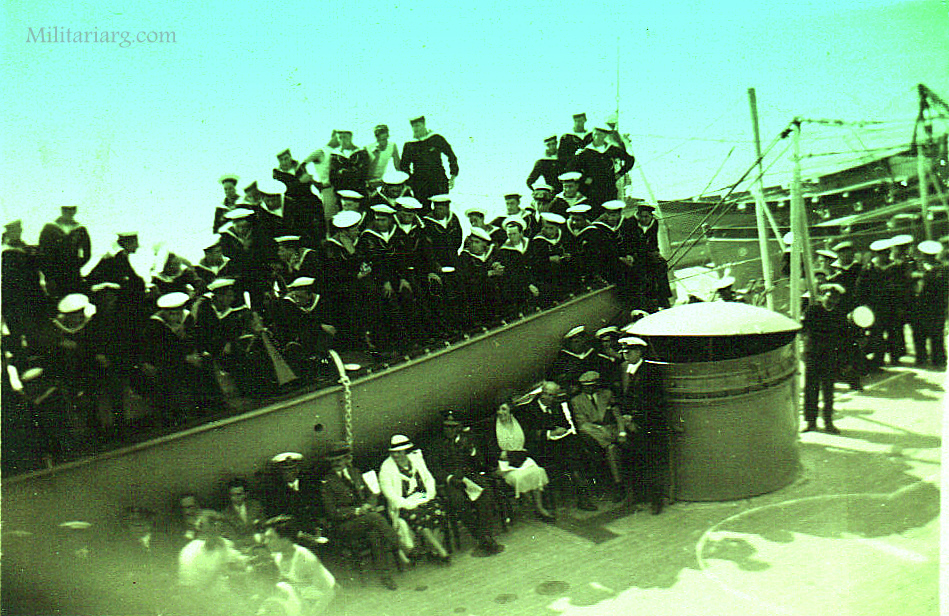
Coastal Artillery Troops, circa 1940s.
Model 1945 uniform. Coastal Artillery and Naval Band
1944.
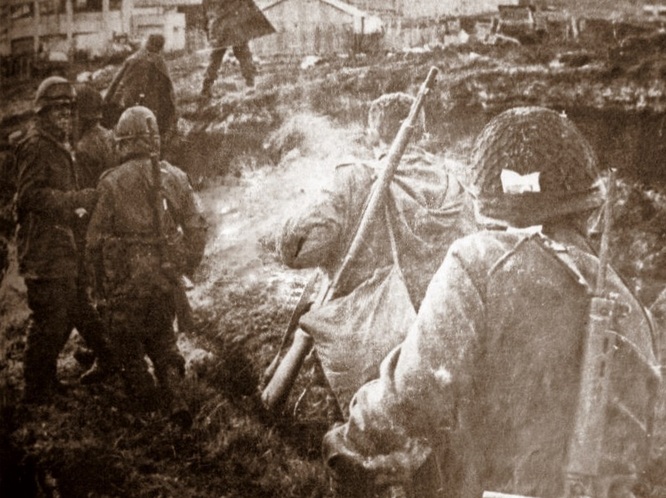
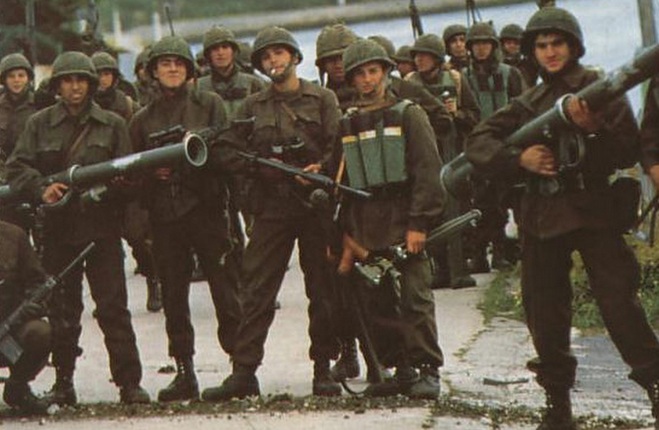
Malvinas War. FAL and Garand-Beretta (?)
M-20 A1B1 Super Bazooka.
FAP replica
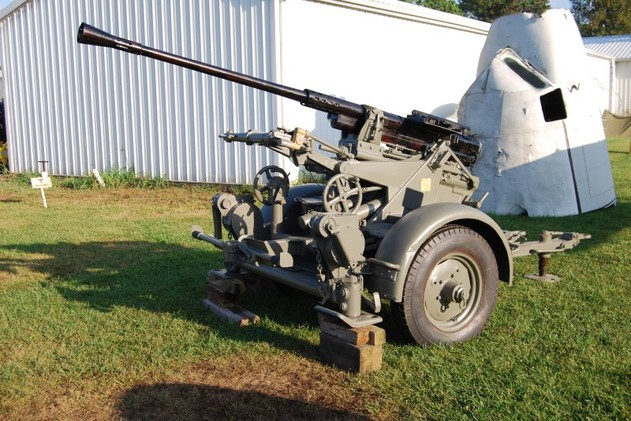
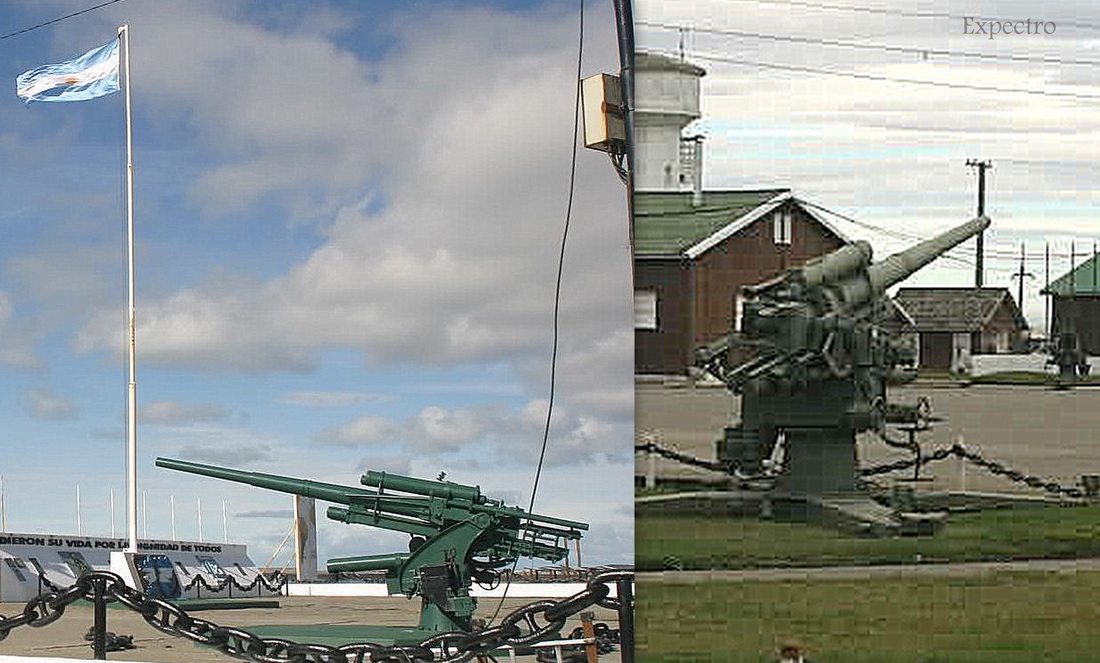
Flak 37 or 3.7cm AG. This weapon first entered service in 1935 as the Flak 18. It was developed in Switzerland by Rheinmetall to avoid restrictions of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. It was orginally called the St 10 or the Solothurn S10-100. Manufacture of the Flak 18 stopped in 1936 but was never withdrawn from service inspite of several design flaws with the utillity of the carriage.The new Flak 36 was basiclly the same gun with improvments in the carriage. it was altered to be towed with only one axel.
http://www.indianamilitarymuseum.org/apps/photos/photo?photoid=13844204
http://www.indianamilitarymuseum.org/apps/photos/photo?photoid=13844204
Bofors Twin 40mm/56 caliiber Anti-Aircraft Gun.
AA Artilley; International Truck.
Prototype 88s were first produced in 1928. These early models, the FlaK 18, used a single-piece barrel with a length of 56 calibres, leading to the commonly-seen designation 88/L56. FlaK is a German contraction of Flugzeugabwehr-Kanone or Flugabwehr-Kanone (hence the capital K) meaning anti-aircraft gun. (Wikipedia)
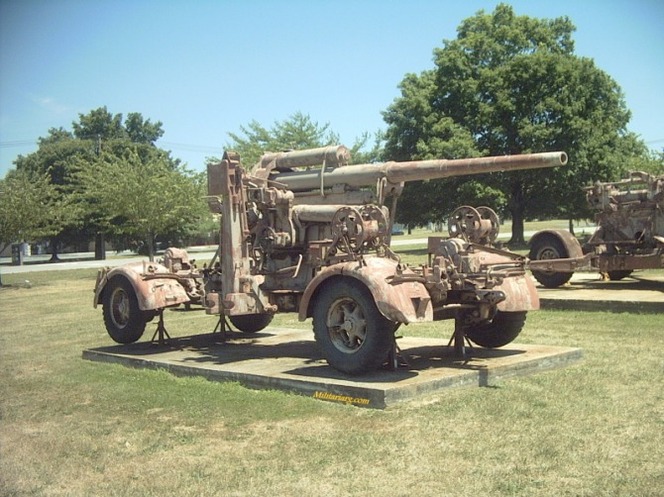
In July 1940 the Argentine Marine Infantry began using Krupp 88 L56 cannons with a central controller Wiko "Wikog" fire guidance system .
In July 1940 the Argentine Marine Infantry began using Krupp 88 L56 cannons with a central controller Wiko "Wikog" fire guidance system .
Krupp 88mm AA. Prototype 88s were first produced in 1928. These early models, the FlaK 18, used a single-piece barrel with a length of 56 calibres, leading to the commonly-seen designation 88/L56. FlaK is a German contraction of Flugzeugabwehr-Kanone or Flugabwehr-Kanone (hence the capital K) meaning anti-aircraft gun.Photo: Omar Expectro.
SCR-299 SCR-299 "mobile communications unit"; Chevy G506 Model G7105 Panel Body K-51 with Ben Hur K-52 generator trailer.
P.A.P.I (Proyectil antitanque para infanteria), DGFM. Rocket-propelled grenade.
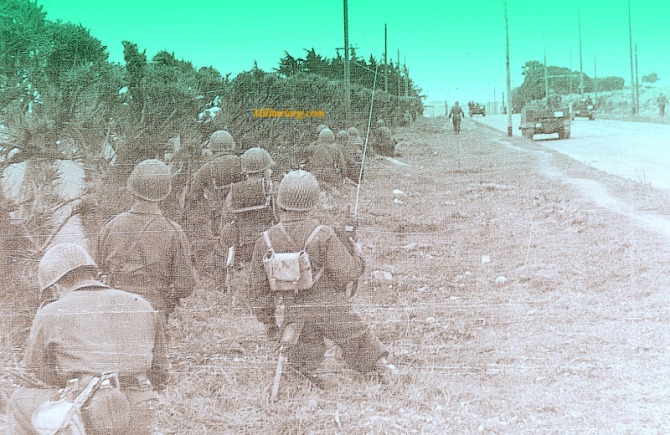
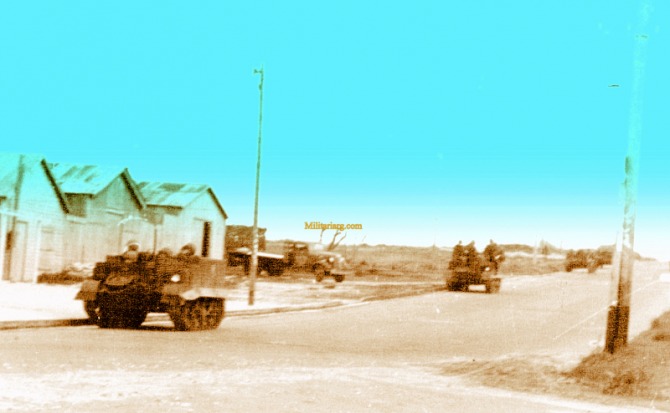
Ford T-16 Universal Carriers and marines with M1 (WWII era), camoflauge w/net and radio set type SCR-536 BC-611 (?) Walkie or Handy Talkie during maneuvers in Mar del Plata circa 1953.
Argentine marine infantry from the 1950s in a column of T16 carriers. The photos are from Mar del Plata on September 7, 1954.
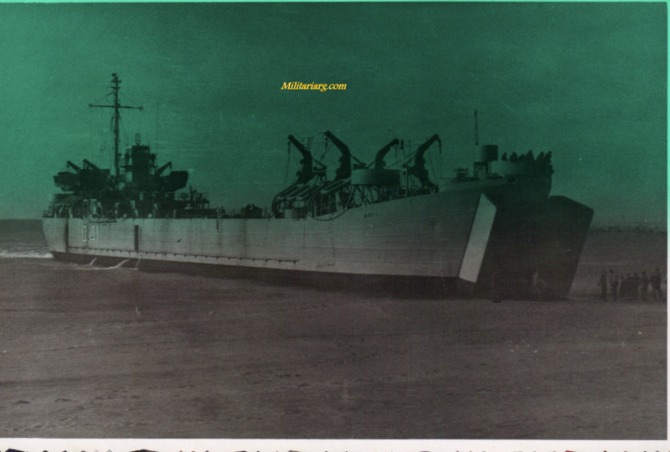
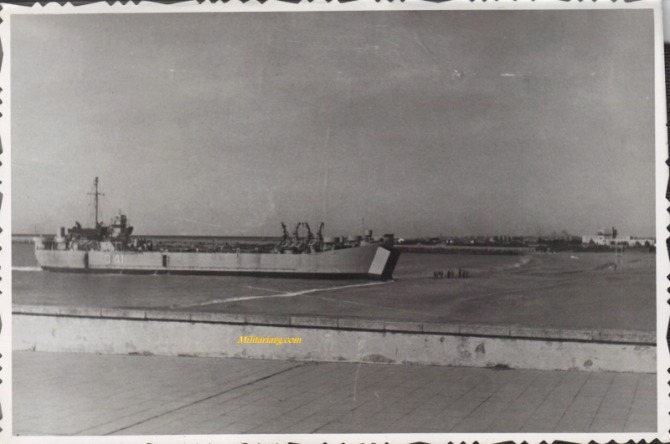
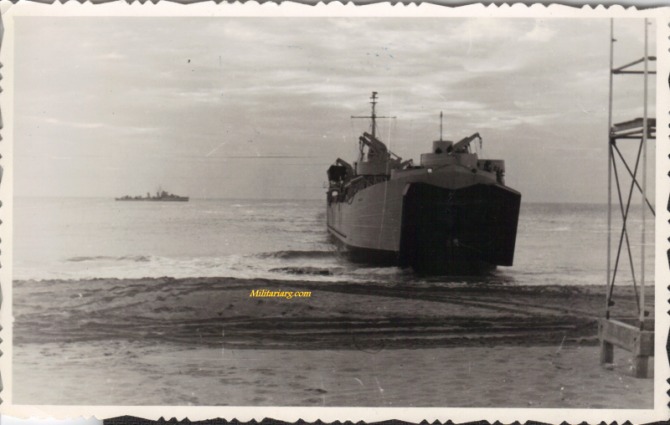
Landing Ship, Tank (LST).
Landing Ship, Tank (LST) was the military designation for naval vessels created during World War II to support amphibious operations by carrying significant quantities of vehicles, cargo, and landing troops directly onto an unimproved shore. Wikipedia.
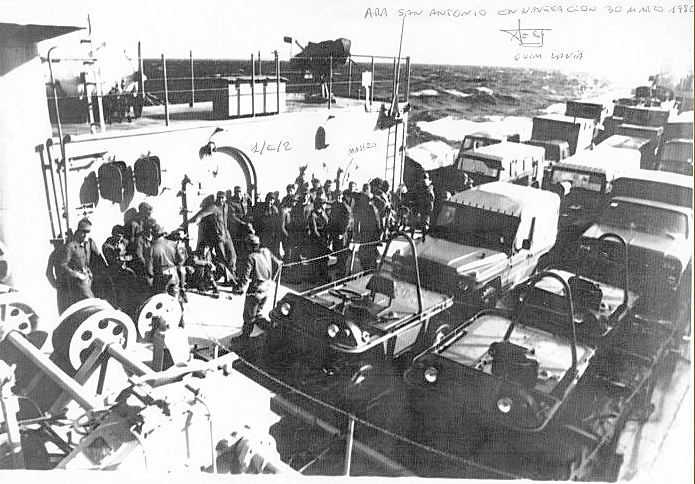
In the 1950s Argentina made its own model of the TSL called ARA Cabo San Antonio (Q42). It was a tank landing ship in the Argentine Navy, built in Argentina at AFNE, Río Santiago shipyard. She was based on the US Navy's De Soto County-class tank landing ship design.
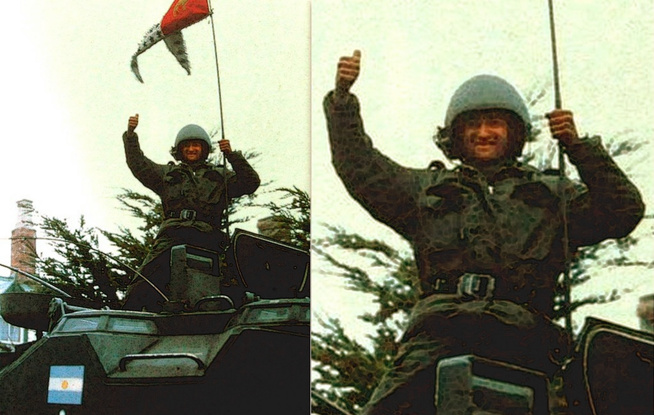
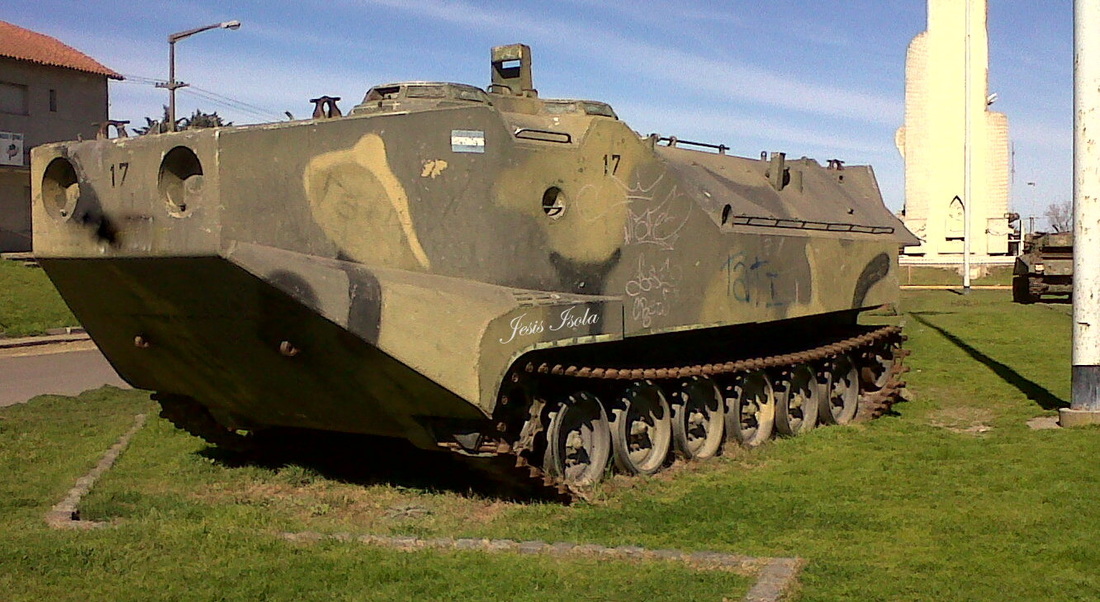
During Malvinas War (1982), The Cabo San Antonio disembarked twenty LVT7 tracked amphibious armoured personnel carriers and LARC-V transports from the 1st Amphibious Vehicles Battalion, carrying D and E Companies of the 2nd Marine Infantry Battalion at Yorke Bay. Wikipedia.
CVC Combat Vehicle Crewman Helmet, the type used for amphibious assault vehicle AAVP7A1 (or originally known as the LVTP7A1). This type of helmet was used during the Malvinas War by the crews of the amphibious assault vehicles in 1982. It is made of some kind of non-ballistic fiberglass but gave some protection to armored crews. It is possible that the design was originally for pilots of the P series. It was made by the US in the 1960s.
Volvo Valp C202 "Laplander" during Malvinas Was.
Volvo "Laplanders". ARA Cabo San Antonio. March 19Citroen Lorth Fardier fl500
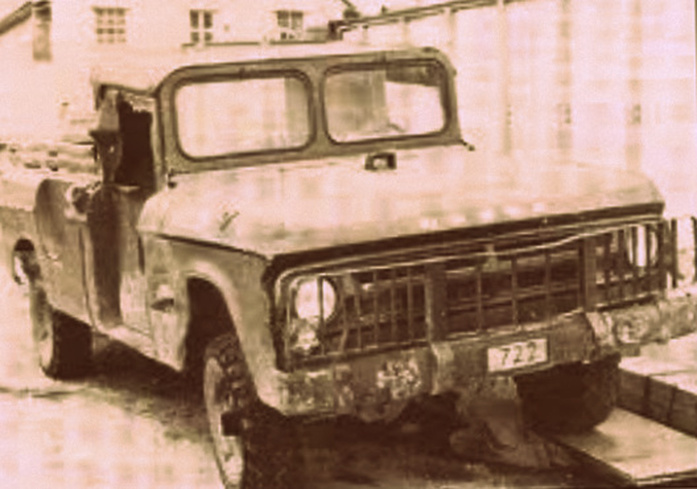
Malvinas War 1982. D200 Dodge. W&T.
1981 Argentine Marines Visor Cap, made by Jose M. Saavedra y Cia SRL.
Marines Infantry Winter Cap
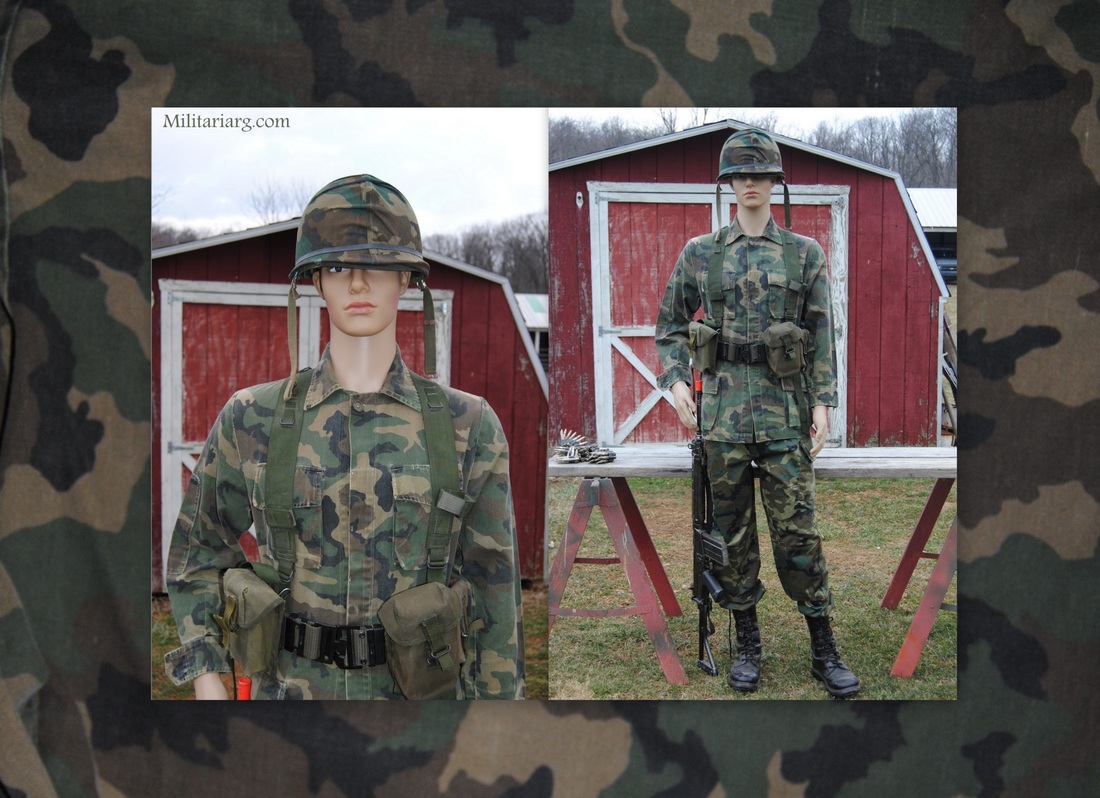
Marines Infantry ERDL Camo.
Recommended read:
History of the Argentine Navy Uniforms by Julio M. Luqui-Lagleyze. Departamento de Estudios Historicos Navales.